The device and principle of operation of the HVAC heating, ventilation and air conditioning system
Content
The problem of maintaining a comfortable temperature in the passenger compartment of a car arose at the dawn of the automotive industry. In order to keep warm, motorists used compact wood and coal stoves, gas lamps. Even exhaust gases were used for heating. But with the development of technology, more convenient and safer systems began to appear that can provide a comfortable climate during the trip. Today, this function is performed by the vehicle's ventilation, heating and air conditioning system - HVAC.
Interior temperature distribution
On hot days, the body of the car gets very hot in the sun. Because of this, the temperature in the passenger compartment rises significantly. If the temperature outside reaches 30 degrees, then inside the car the readings can rise up to 50 degrees. In this case, the most heated layers of air masses are in the zone located closer to the ceiling. This causes increased sweating, increased blood pressure and excessive heat in the driver's head area.
To create the most favorable conditions for a trip, it is necessary to provide the opposite temperature distribution pattern: when the air in the head area is slightly cooler than in the driver's feet. The HVAC system will help provide this warm-up.
System device
The HVAC (Heating Ventilation Air-Conditioning) module includes three separate devices at once. These are heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. The main function of each of them is to maintain comfortable conditions and air temperature in the vehicle interior.
The choice of one or another system is determined by climatic conditions: in the cold season, the heating system is activated, on hot days the air conditioner is turned on in the car. Ventilation is used to keep the air inside fresh.
Heating System in the car includes:
- mixing type heater;
- centrifugal fan;
- guide channels with dampers.
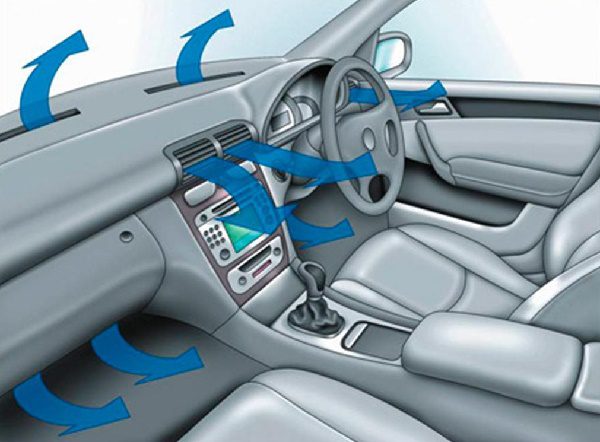
The heated air is directed to the windshield and side windows, as well as to the face and legs of the driver and front passenger. Some vehicles also have air ducts for the rear passengers. Additionally, electrical devices are used to heat the rear and windshields.
Ventilation system helps to cool and clean the air in the car. During ventilation operation, the main elements of the heating system are involved. Additionally, cleaning filters are used that trap dust and trap extraneous odors.
Finally, the air conditioning system able to cool the air and reduce the humidity in the car. For these purposes, an automobile air conditioner is used.
The HVAC system allows not only to provide a comfortable temperature, but also the necessary visibility when the car windows can freeze or fog up.
How air enters the cabin
For heating, air conditioning or ventilation of the passenger compartment, air is used that enters the interior while the vehicle is moving through the inlet provided for this. A high pressure is created in this area, allowing air to flow further into the duct and then into the heater.
If the air is used for ventilation, then its additional heating is not carried out: it enters the passenger compartment through the vents on the center panel. The outside air is pre-cleaned by a pollen filter, which is also installed in the HVAC module.
The device and principle of operation of an automobile stove
The heating of the passenger compartment is carried out with the help of a liquid that cools the engine. It takes heat from the running engine and, passing through the radiator, transfers it to the car interior.
The design of an automobile heater, better known as a "stove", consists of several basic elements:
- radiator;
- coolant circulation pipes;
- fluid flow regulator;
- air ducts;
- dampers;
- fan.
The heating radiator is located behind the dashboard. The device is connected to two tubes that transmit the coolant inside. Its circulation through the vehicle cooling and interior heating systems is provided by a pump.
As soon as the motor heats up, the antifreeze absorbs the heat coming from it. Then the heated liquid enters the stove radiator, heating it like a battery. At the same time, the heater blower blows cold air. Heat exchange takes place again in the system: heated air passes further into the passenger compartment, and colder masses cool the radiator and antifreeze. Then the coolant flows back to the engine, and the cycle is repeated again.
In the passenger compartment, the driver regulates the direction of the heated flows by switching the flaps. Heat can be directed to the face or legs of the motorist, as well as to the windshield of the car.
If you turn on the stove with a cold engine, this will lead to additional cooling of the system. Also, the humidity in the cabin will increase, the windows will start to fog up. Therefore, it is important to turn on the heater only after the coolant heats up to at least 50 degrees.
Air recirculation
The air system of the car can take air not only from the street, but also from the inside of the car. The air masses are then cooled by the air conditioner and fed back into the passenger compartment through the air ducts. This process is called air recirculation.
Recirculation can be activated using a button or switch located on the car's dashboard.
Recirculated air mode allows you to lower the temperature in the passenger compartment faster than when taking in air from the street. The interior air passes through the cooling unit repeatedly, cooling more and more each time. By the same principle, the car can be warmed up.
Recirculation is especially important for people who are sensitive to road dust, pollen and other allergens from the outside. Also, turning off the air supply from the street may become necessary if an old truck or other vehicle is driving in front of you, from which an unpleasant smell is emitted.
However, it is important to take into account that recirculation completely excludes air exchange with the environment. This means that the driver and passengers have to breathe a limited amount of air. Therefore, it is not recommended to use this mode for a long time. Experts advise limiting yourself to a 15-minute interval. After that, you need to connect the air supply from the outside, or open the windows in the car.
How climate management works
The driver can control the heating or cooling of the air in the passenger compartment by manually setting the modes, connecting the air conditioner. In more modern vehicles, the climate control system maintains the set temperature inside the car. The device integrates an air conditioner, heater blocks and a heated or cooled air supply system. Climate control is controlled by sensors installed in the passenger compartment and on individual elements of the system.
For example, the simplest air conditioning unit is equipped with a minimum set of sensors, which include:
- a sensor that determines the air temperature outside;
- a solar radiation sensor that detects radiation activity;
- interior temperature sensors.
The heating, ventilation and air conditioning system is one of the important elements that ensure the comfort of the driver at any time of the year. In the most budget vehicles, the HVAC unit is represented only by a heating and air ventilation system. In most cars, air conditioning is added to their number. Finally, modern models are equipped with a climate control system that automatically regulates the temperature inside the cabin.
