The device and principle of operation of the gearbox
Content
For a car to move on the road, it is not enough to have a powerful and efficient engine under the hood. The torque from the crankshaft must somehow be transmitted to the drive wheels of the vehicle.
For this purpose, a special mechanism was created - a gearbox. Consider its structure and purpose, as well as how different KP modifications differ.
The purpose of the gearbox
In short, the gearbox is designed to transfer torque from the power unit to the drive wheels. The transmission also converts the crankshaft speed so that the driver can accelerate the car without cranking the engine to maximum rpm.

This mechanism is matched to the parameters of the internal combustion engine in order to maximize the entire resource of the engine without damage to its parts. Thanks to the transmission, the machine can move both forward and backward.
All modern cars have a transmission that allows you to temporarily disable the rigid coupling of the crankshaft with the driving wheels. This allows the car to idle, for example, gently approaching a traffic light. This mechanism also allows you not to turn off the engine when the car stops. This is necessary to recharge the battery and to operate additional equipment, such as an air conditioner.

Each commercial proposal must meet the following requirements:
- Provide car traction and economical fuel consumption, depending on the power and volume of the engine;
- Ease of use (the driver should not be distracted from the road when changing the vehicle speed);
- Do not make noise during operation;
- High reliability and efficiency;
- Minimum dimensions (as much as possible in the case of powerful vehicles).
Transmission device
Throughout the history of the automotive industry, this mechanism has been constantly modernized, due to which today there is a wide variety of transmissions that have many significant differences.

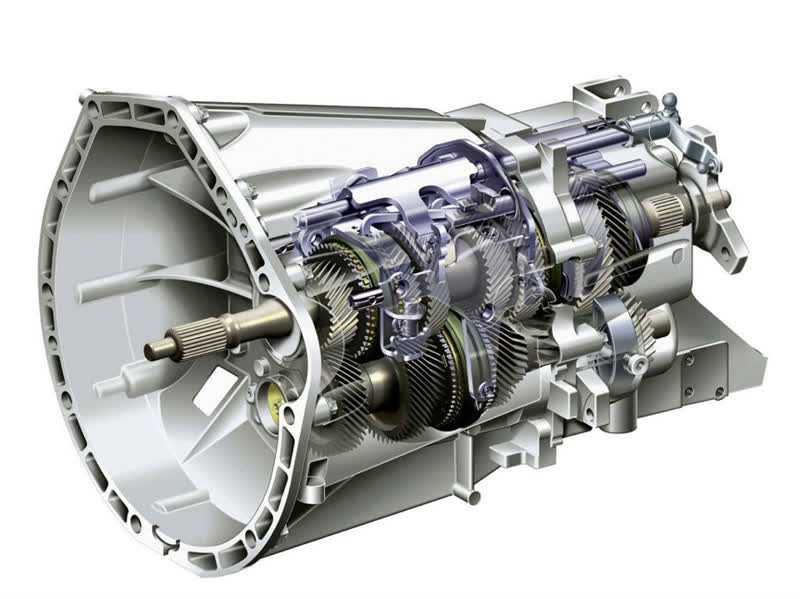
The device of any gearbox includes:
- Housing. It contains all the necessary parts that ensure the coupling of the motor to the drive shaft, from which the rotation is transmitted to the wheels.
- Oil reservoir. Since in this mechanism the parts come into contact with each other under a heavy load, the lubrication ensures their cooling and creates an oil film that protects against premature wear on the gears.
- Speed transmission mechanism. Depending on the type of box, the mechanism may include shafts, a set of gears, a planetary gearbox, a torque converter, friction discs, belts and pulleys.
KP classification
There are several parameters by which all boxes are classified. There are six such signs. In each of them, the torque is supplied to the drive wheel according to its own principle and has a different method of gear selection.
By way of transmission of power flow
This category includes the following KPs:
- Mechanical gearbox. In this modification, the power take-off is performed by a gear drive.
- Gearbox with coaxial shafts. Rotation is also transmitted through a gear train, only its elements are made in a conical or cylindrical shape.
- Planetary. Rotation is transmitted through a planetary gear set, the gears of which are located in one plane.
- Hydromechanical. In such a transmission, a mechanical transmission (mostly planetary type) is used in conjunction with a torque converter or fluid coupling.
- CVT. This is a type of gearbox that does not use a step transmission. Most often, such a mechanism works together with a fluid coupling and a belt connection.

By the number of main shafts with gears
When classifying gearboxes by the number of shafts, they are distinguished:
- With two shafts and one-stage gearing of the axle. There is no direct drive in these transmissions. Most often, such modifications can be found in front-wheel drive cars. Some models with rear-mounted motors also have a similar box.
- With three shafts and two-stage axle gearing. In this category, there are versions with coaxial and non-coaxial shafts. In the first case, there is a direct transmission. In cross-section, it has smaller dimensions, and slightly larger in length. Such boxes are used in rear-wheel drive cars. The second subcategory has no direct transmission. Basically, this modification is used in four-wheel drive vehicles and tractors.

- With multiple shafts. In this gearbox category, the shafts can have a sequential or non-sequential number of engagement. These gearboxes are mainly used in tractors and machine tools. This allows for more gears.
- Without shafts. Such checkpoints are not used in ordinary transport. Among such models there are coaxial and non-aligned versions. They are mainly used in tanks.
Classification of planetary gearboxes
Planetary gearboxes are divided according to the following parameters:
- Two, three, four or more degrees of freedom when all friction elements are disconnected;
- The type of planetary gear used in the mechanism is epicyclic (the main crown has an internal or external arrangement of teeth).
By control method
In this category, there are such boxes:
- Manual. In such models, the driver selects the desired gear. There are two types of manual transmissions: shifting is done by the driver's efforts or through a servo drive. In both cases, the control is carried out by a person, only the second category of the gearbox has a servo device. It receives a signal from the driver, and then sets the selected gear. The machines most often use a hydraulic servo drive.
- Automatic. The electronic control unit determines several factors (the degree of pressing the accelerator, the load coming from the wheels, the crankshaft speed, etc.) and on the basis of this it determines when to engage an up or down gear.

- Robot. This is an electromechanical box. In it, the gears are turned on in automatic mode, only its device is like that of ordinary mechanics. When the robotic transmission is working, the driver does not participate in gear shifting. The control unit itself determines when to engage which gear. In this case, switching occurs almost imperceptibly.
By the number of gears
This classification is the simplest. In it, all boxes are divided by the number of gears, for example, four, five six, and so on. This category includes not only manual but also automatic models.
Gearbox Types
The most common classification is by the type of the box itself:
- Mechanics. In these models, gear selection and shifting is done entirely by the driver. Basically it is a gearbox with several shafts, which works through a gear train.
- Machine. This transmission works in automatic mode. The selection of a suitable gear is carried out based on the parameters that are measured by the gearbox control system.
- The robot is a kind of mechanical gearbox. The design of this modification is practically no different from conventional mechanics: it has a clutch, and the gears are engaged through the connection of the corresponding gear on the driven shaft. Only the gear control is controlled by the computer, not the driver. The advantage of such a transmission is the smoothest shifting possible.
Design-specific gearboxes
In addition to known transmissions, unique modifications can also be used in vehicles. These types of boxes have a specific design, and with it their own operating principle.
Bezvalnaya KP
Transmissions that do not use pre-assembled shafts are called shaftless. In their design, they have several rows of gears located in two parallel axes. The gears are connected by locking the clutches.

The gears are located on two shafts. Two of them are fixed tightly: on the leader it is installed in the first row, and on the follower - in the last. The intermediate gears located on them can play the role of a leading or driven, depending on the generated gear ratio.
This modification allows the transmission ratio to be increased in both directions. Another advantage of such a transmission is the increased power range of the box. One of the most serious drawbacks is the mandatory presence of an auxiliary automatic system with the help of which gear changes are carried out.
Unsynchronized gearbox
Another type of specific boxes is an unsynchronized one, or one in the design of which the presence of synchronizers is not provided. It can be a permanent mesh type or slip gear type.

To change gear in such a box, the driver must have a certain skill. He must be able to independently synchronize the rotation of gears and couplings, determining the transition time from gear to gear, as well as equalizing the speed of rotation of the crankshaft with the accelerator. Professionals refer to this procedure as rebasing or double squeezing the clutch.
To perform smooth shifting, the driver must have experience in operating such mechanisms. A similar type of transmission is installed in American tractors, motorcycles, sometimes in tractors and sports cars. In modern unsynchronized transmissions, the clutch can be omitted.
Cam gearbox
Cam boxes are a kind of unsynchronized model. The difference is the shape of the meshing teeth. To improve the efficiency of the gearbox, a rectangular shape or cam profile of the teeth is used.

Such boxes are very noisy, therefore they are used in light vehicles mainly on racing cars. During the competition, this factor is not paid attention to, but in an ordinary car such a transmission will not provide an opportunity to enjoy the ride.
Sequential KP
A sequential gearbox is a type of transmission in which the downshift or upshift is carried out exclusively by one step. To do this, a handle or foot switch (on motorcycles) is used, which allows you to move the gear in the basket only one position at a time.

An automatic transmission like Tiptronic has a similar principle of operation, but it only imitates the action of this transmission. The classic sequential gearbox is installed in F-1 cars. Switching speed in them is carried out using paddle shifters.
Preselective CP
In the classic version, the preselective gearbox required a preliminary selection of the next gear before the gearbox switched to it. It often looked like this. While the car was moving, the driver put the next gear on the selector. The mechanism was preparing to shift, but it did so on command, for example, after pressing the clutch.
Previously, such gearboxes were used in military equipment with an unsynchronized, shaftless or planetary transmission. Such box modifications made it easier to operate complex mechanisms until synchronized mechanical and automatic boxes were developed.

Currently a preselection box is used, but it is more commonly referred to as a dual clutch transmission. In this case, the computer itself prepares the transition to the desired speed by connecting a suitable shaft with the gear engaged to the unfixed disk in advance. Another name for this type in modern design is a robot.
Choice of gearbox. What's better?
Many of the listed gearboxes are used only on special equipment or in machine tools. The main gearboxes, which are widely used in light vehicles, are:
- Manual Transmission. This is the simplest type of transmission. In order for the rotational movement to be transmitted from the power unit to the gearbox shaft, a clutch basket is used. By pressing the pedal, the driver disconnects the drive shaft of the box from the motor, which allows him, without harm to the mechanism, to select a gear suitable for a given speed.

- Automatic transmission. The torque from the motor is supplied through a hydraulic transmission (torque converter or fluid coupling). The working fluid acts as a clutch in the mechanism. It drives, as a rule, a planetary gearbox. The entire system is controlled by an electronic control unit that analyzes data from many sensors and selects the gear ratio accordingly. Among the automatic boxes, there are many modifications that use different operating schemes (depending on the manufacturer). There are even automatic models with manual control.

- Robotic transmission. These KPs also have their own varieties. There are electric, hydraulic and combined types. In design, the robot is basically similar to a manual transmission, only with a dual clutch. The first supplies torque from the motor to the drive wheels, and the second automatically prepares the mechanism for engaging the next gear.

- CVT transmission. In a common version, the variator consists of two pulleys, which are interconnected by a belt (one or more). The principle of operation is as follows. The pulley moves apart or shears, causing the belt to move to a larger or smaller diameter element. From this, the gear ratio changes.

Here is a comparison chart of each type of box with their advantages and disadvantages.
| Box type: | Principle of operation | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| MKPP | Manual shifting, synchronized gearing. | Simple structure, cheap to repair and maintain, saves fuel. | A beginner needs to get used to the synchronized operation of the clutch and gas pedal, especially when starting up a hill. Not everyone can turn on the right gear right away. Requires smooth use of the clutch. |
| Automatic transmission | The hydraulic pump creates the pressure of the working fluid, which drives the turbine, and that transmits the rotation to the planetary gear. | Drive comfortably. Does not require driver intervention in the gearshift process. Changes gears, making the most of the entire engine resource. Eliminates the human factor (when the driver accidentally turns on the first speed instead of the third). Shifts gears smoothly. | High maintenance cost. The mass is greater than that of the manual transmission. Compared to the previous type of transmission, this one will result in higher fuel consumption. Efficiency and dynamics are lower, especially with a sporty driving style. |
| Robot | The dual clutch allows you to prepare the next gear for engagement while driving. Most often, even transmissions are tied to one group, and odd ones to the other. Internally similar to a mechanical box. | Maximum smoothness of switching. Does not require driver intervention in the work process. Economical fuel consumption. High efficiency and dynamics. Some models have the ability to select the operating mode. | The complexity of the mechanism leads to its low reliability, frequent and expensive maintenance. Poorly tolerates difficult road conditions. |
| Variator (CVT) | The torque is transmitted using a torque converter, as in an automatic machine. Gear shifting is carried out by moving the drive shaft pulley, which pushes the belt to the desired position, which increases or decreases the gear ratio. | Switching without jerks, more dynamic compared to a conventional machine. Allows a little fuel savings. | It is not used in powerful power units, since the transmission is belt. High maintenance cost. Requires the correct operation of the sensors, from which the signal is received for the operation of the CVT. Poorly tolerates difficult road conditions and does not like towing. |
When deciding on the type of transmission, it is necessary to proceed not only from financial capabilities, but more focus on whether this box is suitable for the car. It is not for nothing that manufacturers from the factory pair each power unit with a specific box.
A manual transmission is more suitable for an active driver who understands the intricacies of high-speed car control. The machine is more suitable for those who like comfort. The robot will provide reasonable fuel consumption and is adapted for measured driving. For lovers of the most smooth operation of the machine, a variator is suitable.
In terms of technical specifications, it is impossible to point to a perfect box. Each of them is good in its own conditions and with specific driving skills. In one case, it is easier for a beginner to start by operating a variety of automatic transmissions; in another, it is preferable to develop the skill of using mechanics.
Questions and answers:
How does the gearbox work? The manual transmission consists of a set of gears that form different gear ratios. The automatic transmission is equipped with a torque converter and variable-diameter pulleys (variator). The robot is an analogue of mechanics, only with a double clutch.
What's inside the gearbox? Inside any gearbox there is a drive shaft and a driven shaft. Depending on the type of box, either pulleys or gears are installed on the shafts.







