Types of automotive oils: which ones exist and how to identify them?
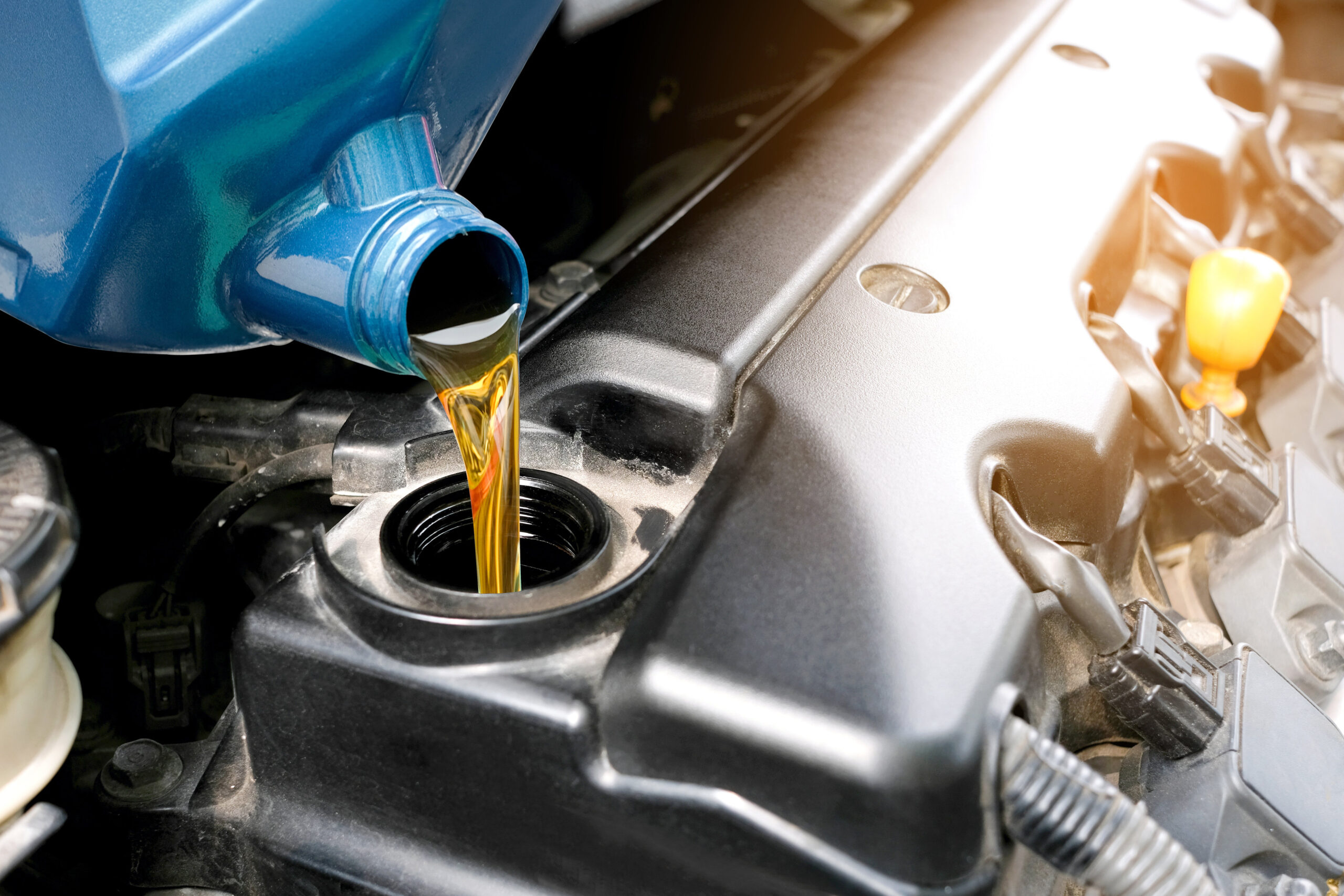
Automotive oil is a substance composed of base oil and additives that performs vital functions for an engine.
For example: minimizing wear caused by friction between moving parts, preventing corrosion, protecting the system from emissions, and properly distributing heat until the engine temperature drops.
What types of automobile oils exist and how to identify them?
Before buying and applying automotive oil, pay attention to the codes on the packaging labels. They will explain the purpose of the oil and how to use it correctly.
Choosing the right product is only possible if you know what coding the engine oil for your car should have according to the characteristics of each car. Different types of automobile oils can be classified in the following ways. Let's take a closer look.
Automotive oils, depending on engine type:
- Gasoline engine oil. This automotive oil is identified by the letter S followed by another letter of the alphabet. The second letter represents its quality, the more you drive, the higher the quality of oil you need. By the way, SN is the highest value for gasoline engines.
- Diesel engine oil. Diesel engine oils are identified with a letter. C is followed by another letter of the alphabet. Like gasoline motor oil, its quality is determined by the order of the letters of the alphabet. The highest quality marking is CJ-4.
Automotive viscosity grade oils:
- Monograde automotive oil. This type of automotive oil has a unique viscosity grade that can be 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50 or 60. This grade remains in a stable temperature range.
- Universal automotive oil. This type has different degrees of viscosity depending on temperature, which allows it to be denser in summer and more liquid in winter. An example is SAE 15W-40, the name of which has the following meaning: 15W represents the oil viscosity at low temperatures. The lower this number, the better its performance at low temperatures; W means the oil can be used in winter; 40 represents the oil viscosity at high temperatures.

Automotive oils, depending on their production... Depending on the type of production, automobile oil can be mineral or synthetic. In these cases, there is no standardized coding (specific letter) that determines which oil is mineral and which is synthetic. Only the label indicates the type of oil sold.
- Mineral oil for cars. It is a crude oil refining product with a minimum amount of additives. A feature of mineral oil is that it is not well suited for use at significant temperature extremes, as it can freeze in the engine in severe frost. This can cause wear during cold starts. Moreover, the molecules of mineral motor oil are heterogeneous. As a result, at some point they begin to collapse, and the oil quickly loses its function. That is why the mineral water requires more frequent replacement, on average every 5 kilometers.
- Synthetic car oil... This is the synthesis of base oils based on synthetics, as well as additives that give it useful properties (increased wear resistance, purity, protection against corrosion). Such oils are suitable for operation in the most modern engines and in extreme operating conditions (low and high temperatures, high pressure, etc.). Synthetic oil, unlike mineral oil, is produced on the basis of directed chemical synthesis. In the process of its production, crude oil, which is the basic element, is distilled and then refined into basic molecules. Then, on their basis, a base oil is obtained, to which additives are added so that the final product has exceptional characteristics.
Questions and answers:
What types of car oils are there? Motor (for two-stroke and four-stroke engines), transmission, diesel (for diesel units), mineral, semi-synthetic, synthetic.
What kind of engine oils are used in modern engines? Basically, modern cars use semi-synthetics (Semi-Synthetic) or synthetics (Synthetic). Less often, mineral water is poured into the motor (Mineral).