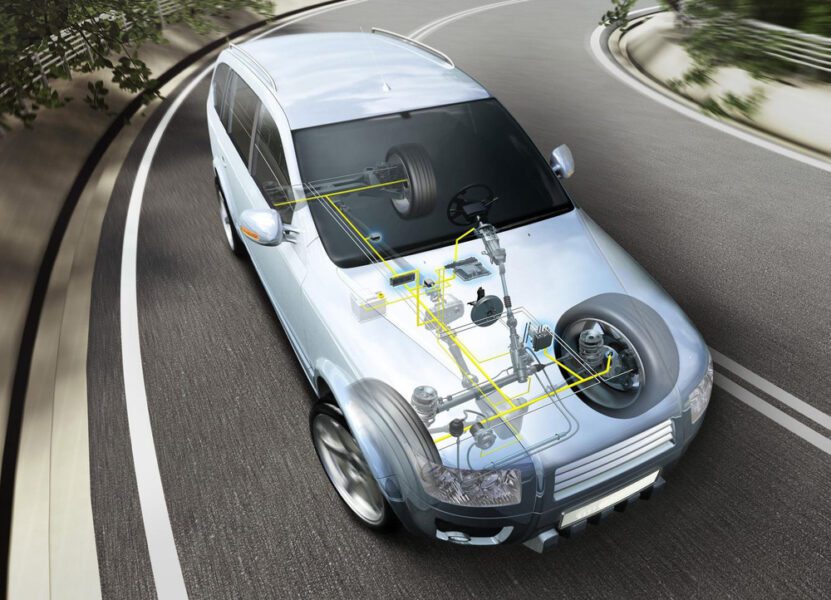
TSC, ABS and ESP systems. Principle of operation
Content
Modern cars are getting smarter and safer. It is impossible to imagine that a brand new car will be without ABS and ESP. So, let's take a closer look at what the above abbreviations mean, how they work and help drivers to drive safely.
What is ABS, TSC and ESP
Between ABS, TCS and ESP there are common points related to stabilization of the vehicle's motion at critical moments (hard braking, sharp acceleration and skidding). All devices monitor the behavior of the car on the road and are connected in a timely manner where necessary. It is also important that a vehicle equipped with a minimum set of traffic safety systems reduces the likelihood of getting into an accident many times. More details about each system.

Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
The Anti-Lock Brake System is one of the earliest electronic assistive devices to prevent wheel lockup on wet and slippery roads, as well as when the brake pedal is pressed hard. Protozoa
ABS consists of the following components:
- control unit with an executive unit that distributes pressure;
- wheel speed sensors with gears.
Today the anti-lock braking system works in integration with other traffic safety systems.

Traction system control (TSC)
Traction control is an addition to ABS. This is a complex of software and hardware device that prevents slipping of the driving wheels at the necessary moment.

Electronic stability program (ESP)
ESP is an electronic vehicle stability control system. It was first installed in 1995 on a Mercedes-Benz CL600. The main task of the system is to control the lateral dynamics of the car, preventing it from skidding or side sliding. ESP helps to keep directional stability, not to go off track on the road with poor coverage, especially at high speed.
Principle of operation
ABS
While the car is moving, wheel rotation sensors are constantly working, sending a signal to the ABS control unit. When you press the brake pedal, if the wheels are not locked, the ABS will not work. As soon as one wheel begins to block, the ABS unit partially restricts the supply of brake fluid to the working cylinder, and the wheel rotates with constant short braking, and this effect is well felt with the foot when we press on the brake pedal.
The principle of operation of the anti-lock braking system is based on the fact that during sharp braking there is the possibility of maneuvering, because without the ABS, when the steering wheel is rotated with full braking, the car will continue to go straight.
ESP
The stability control system works by receiving information from the same wheel rotation sensors, but the system requires information only from the drive axle. Further, if the car is skidding, there is a risk of skidding, the ESP partially restricts the fuel supply, thereby reducing the speed of movement, and will work until the car continues in a straight line.
TCS
The system works according to the ESP principle, however, it can not only limit the engine operating speed, but also adjust the ignition angle.

What else can an "anti-slip setting" do?
Opinions that antibuks only allows you to level the car and get out of the snowdrift is wrong. However, the system helps in some situations:
- at a sharp start. Especially useful for front-wheel drive vehicles with half-axles of different lengths, where at a sharp start the car leads to the right side. Here the anti-skid comes into play, which brakes the wheels, equalizing their speed, which is especially useful on wet asphalt when good grip is required;
- snow track. Surely you have driven on unclean roads more than once, and after the pioneers of the snow road, a track remains, and if it was a truck or even an SUV, then a deep track in a high snow “strip” between the wheels will remain of it. When overtaking a car, crossing such a track, the car can instantly be thrown to the side of the road or twisted. Antibuks counteracts this by correctly distributing torque to the wheels and metering the engine speed;
- cornering. When making a turn, on a slippery road, the car can spin around its axis at the moment. The same applies to the movement along a long turn, where with the slightest movement of the steering wheel you can “fly away” into the ditch. Antibuks intervenes in any of the cases and tries to align the car as much as possible.
How does the automatic transmission protect?
For the transmission, the presence of a number of safety systems has a beneficial effect. This is especially true of an automatic transmission, for which each slip, contaminating oil with wear products of friction linings, reduces the resource of the unit. This also applies to the torque converter, which also “suffers” from slipping.
In manual transmissions, front-wheel drive cars, the differential fails from slipping, namely, the satellites “stick” to the driven gear, after which further movement is impossible.
The bad points
The auxiliary electronic systems also have negative aspects that emerged during operation:
- torque limitation, especially when fast acceleration is required, or the driver decides to test the “strength” of his car;
- in budget cars, the ESP systems are inadequate, where the car simply refused to leave the snowdrift, and the torque was cut to an impossible minimum.

Can I turn it off?
Most cars equipped with anti-skid and other similar systems provide for the forced shutdown of the function with a key on the instrument panel. Some manufacturers do not provide this opportunity, justifying the modern approach to active safety. In this case, you can find the fuse responsible for the operation of the ESP and remove it. Important: when disabling the ESP in this way, ABS and related systems may stop functioning, so it is better to abandon this idea.
Questions and answers:
What are ABS and ESP? ABS is an anti-lock braking system (prevents the wheels from locking when braking). ESP - a system of exchange rate stability (does not allow the car to go into a skid, independently braking the necessary wheels).
What does ABS EBD mean? EBD - Electronic brakeforce distribution. This is an option, part of the ABS system, which makes emergency braking more efficient and safer.
What is the button in the ESP car? This is the button that activates the option that stabilizes the vehicle on slippery surfaces. In critical situations, the system prevents side sliding or skidding of the car.
What is ESP? This is the stability control system, which is part of the braking system equipped with ABS. ESP independently brakes with the desired wheel, preventing the car from skidding (it is activated not only during braking).