Waste motor oils. Composition and calculation
Waste synthetic and semi-synthetic motor oils
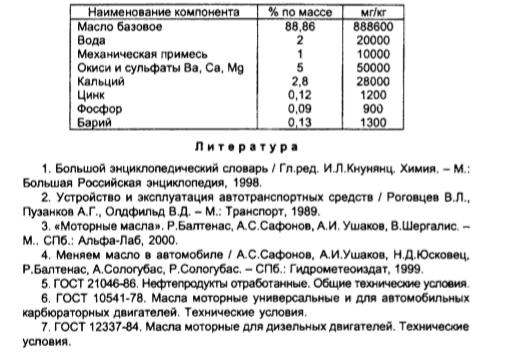
Waste oil products contain 10 to 30 chemicals. Among them are lead, zinc and other heavy metals, as well as calcium, phosphorus and polycyclic organic compounds. Such components are resistant to decay, poison the soil, water, and also cause cellular mutations in plants and humans.
- Mineral oils have a fractional composition of oil refining and contain almost no additives, stabilizers and halogen reagents.
- Semi-synthetic lubricants are obtained by modifying natural oils by introducing additives.
- Synthetic analogues are the product of chemical synthesis.
Regardless of origin, lubricating fluids include alkanes with a carbon number of C12 - FROM20, cyclic aromatic compounds (arenes) and naphthene derivatives.


As a result of operation, oils are exposed to thermal stress. As a result, organic cycles and naphthenes are oxidized, and paraffin chains break up into shorter ones. Additives, modifiers and asphalt-resinous substances precipitate. In this state, the oil does not meet operational requirements, and the engine is running for wear. Waste products are released into the atmosphere and pose an environmental threat.
Recycling and Disposal Methods
Oily waste is recovered if the process is economically viable. Otherwise, waste materials are burned or buried. Regeneration methods:
- Chemical recovery - sulfuric acid treatment, alkaline hydrolysis, calcium carbide treatment.
- Physical purification - centrifugation, settling, multi-stage filtration.
- Physical and chemical methods - rectification, ion-exchange filtration, extraction, adsorption separation, coagulation.


Oil waste unsuitable for regeneration is purified from heavy metals, emulsion water, and heat-resistant compounds. The resulting liquid is used as fuel for boiler plants. The calculation of the waste is made in accordance with the formula:
Мmmo = Kcl× Кв× ρм× ∑ Viм× Kietc.× Ni× Li / NiL× 10-3,
where: Мmmo - the amount of oil obtained (kg);
Кcl - plum index;
Кв - correction factor for the percentage of water;
ρм — waste density;
Viм - the amount of lubricating fluid poured into the system;
Li — mileage of the hydraulic unit per year (km);
НiL - the rate of annual mileage;
Кietc. is the impurity index;
Ni - the number of operating installations (engines).


Hazard Class
Liquid waste from automotive, aviation and other lubricants is classified as a third hazard class. Chemically resistant compounds of the naphthenic series pose a threat to the environment. Such cyclic reagents lead to changes in plant DNA, autosomal and oncological diseases in humans. Heavy metals cause cellular damage to the kidneys, lungs and other organs. Organochlorine and organophosphorus substances of flame retardants in synthetic oils provoke coughing, shortness of breath, and in severe cases lead to respiratory arrest. The harmful waste of motor oils is reducing the population of birds and other animals.


Watch this video on YouTube