How to check the density of antifreeze?
Content
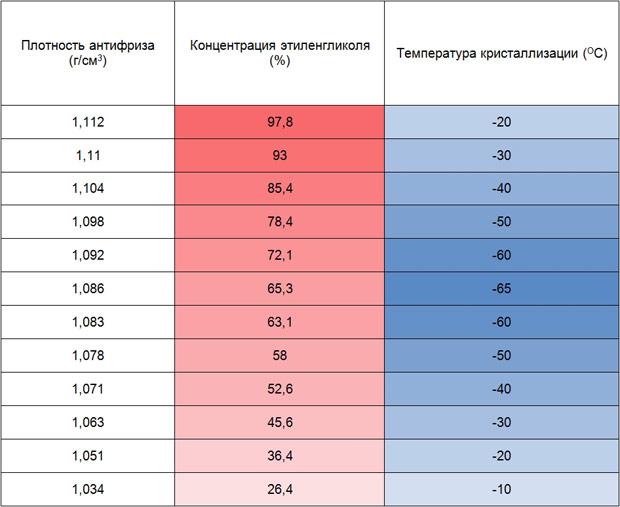
The density of antifreeze depending on the concentration of ethylene glycol
Antifreeze, in a nutshell, is a domestic antifreeze. That is, a liquid with a low freezing point for the engine cooling system.
Antifreeze consists of two main components: water and ethylene glycol. More than 90% of the total volume is made up of these liquids. The rest is antioxidant, antifoam, protective and other additives. A dye is also added to the antifreeze. Its purpose is to indicate the freezing point of a liquid and to indicate wear.
The density of ethylene glycol is 1,113 g/cm³. The density of water is 1,000 g/cm³. Mixing these liquids will give a composition whose density will be between these two indicators. However, this dependence is non-linear. That is, if you mix ethylene glycol with water in a 50/50 ratio, then the density of the resulting mixture will not be equal to the average value between the two densities of these liquids. This is due to the fact that the size and spatial structure of the molecules of water and ethylene glycol differ. The water molecules are somewhat smaller and they take up space between the ethylene glycol molecules.


For antifreeze A-40, the average density at room temperature is approximately 1,072 g / cm³. In A-65 antifreeze, this figure is slightly higher, approximately 1,090 g / cm³. There are tables that list the density values \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbfor antifreeze of different concentrations depending on temperature.
In its pure form, ethylene glycol begins to crystallize at about -12 °C. From 100% to about 67% ethylene glycol in the mixture, the pour point moves towards a minimum and reaches a peak at -75 °C. Further, with an increase in the proportion of water, the freezing point begins to rise towards positive values. Accordingly, the density also decreases.
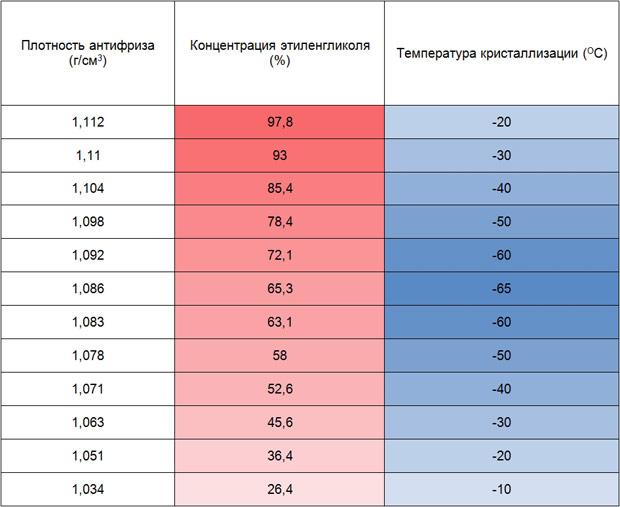

The dependence of the density of antifreeze on temperature
A simple rule works here: with decreasing temperature, the density of antifreeze increases. Let's take a brief look at the example of antifreeze A-60.
At temperatures close to freezing (-60 °C), the density will fluctuate around 1,140 g/cm³. When heated to +120 ° C, the density of antifreeze will approach the mark of 1,010 g / cm³. That is almost like pure water.
The so-called Prandtl number also depends on the density of antifreeze. It determines the ability of the coolant to remove heat from the source of heating. And the greater the density, the more pronounced this ability.


How to check the density of antifreeze?
To assess the density of antifreeze, as well as to check the density of any other liquid, a hydrometer is used. It is advisable to use a hydrometer specially designed for measuring the density of antifreeze and antifreeze. The measurement procedure is quite simple.


- Take a portion of the test mixture into a narrow deep container, sufficient for free immersion of the hydrometer (most devices are equipped with a standard measuring flask). Find out the temperature of the liquid. It is best to measure at room temperature. To do this, you first need to let the antifreeze stand in the room for at least 2 hours so that it reaches room temperature.
- Lower the hydrometer into a container with antifreeze. Measure the density on the scale.
- Find your values in the table with the dependence of the density of antifreeze on temperature. At a certain density and ambient temperature, there can be two ratios of water and ethylene glycol.


In 99% of cases, the correct ratio will be the one where there is more water. Since it is not economically feasible to make antifreeze based mainly on ethylene glycol.
The technology for measuring the density of antifreeze in terms of the procedure itself is no different. However, it is necessary to apply the obtained data in terms of estimating the concentration of the active substance for different types of antifreezes in different ways. This is due to the different chemical compositions of these coolants.


Watch this video on YouTube
