What is an engine turbocharger
Content
- What is a turbine or turbocharger in a car?
- The principle of operation of an automobile turbine
- Turbocharger design
- Turbine (turbocharger) functions
- Types and characteristics of the turbocharger
- What is turbo lag (turbo pit)?
- What is the difference between a turbocharger and a turbocharger (turbocharging)?
- Turbocharger service life
- Operation and maintenance of automotive turbines
- What can break down in a car's turbocharger?
- Is it possible to repair a turbine in a car
- Questions and answers:
Until a few decades ago, turbo engines were perceived as an element of fantastic cars from the future or beautiful computer games. And even after the implementation of the ingenious idea of a simple way to increase engine power, this opportunity has long remained the prerogative of gasoline devices. Now almost every car that comes off the assembly line is equipped with a turbo system, regardless of what fuel it runs on.

At high speeds or steep climbs, the normal engine of the car is seriously overloaded. To facilitate its work, a system was invented that could increase the power of the motor without interfering with the internal structure.
Along with influencing the potential of the engine, the principle of "turbo" contributes to significant purification of exhaust gases, through their reuse and recycling. And this is important for improving the ecology, which meets the requirements of many international organizations fighting to preserve the environment.
Turbocharging has some disadvantages associated with premature ignition of the combustible mixture. But this side effect - the reason for the rapid wear of the pistons in the cylinders - is successfully handled by the correctly selected oil, which is necessary for lubricating the parts during the operation of the turbo engine.
What is a turbine or turbocharger in a car?
The efficiency of a car equipped with a "turbo" increases by 30 - 50%, or even 100%, of its standard capabilities. And this despite the fact that the device itself is relatively inexpensive, has an insignificant weight and volume, and operates reliably according to an ingeniously simple principle.
The device creates an increased pressure in the internal combustion engine due to the artificial injection of an additional dose of air, which forms an increased volume of the fuel-gas mixture, and when it burns, the engine power increases by 40-60%.
A turbo-equipped mechanism becomes much more efficient without changing its design. After installing an unpretentious device, a low-power 4-cylinder engine can deliver the potential of 8-cylinder operation.
To put it more easily, a turbine is an unobtrusive but highly efficient part on the engine of a car that helps increase the performance of the "heart" of the car without unnecessary fuel consumption by recycling the energy of the exhaust gases.
What engines are turbochargers installed on
The current equipment of machines with turbine mechanisms is much faster than their initial introduction into gasoline engines. To determine the optimal mode of operation, the devices were initially used on racing cars, thanks to which they began to apply:
· Electronic control;
· Liquid cooling of the device walls;
· More advanced types of oil;
· Heat-resistant materials for the body.
More sophisticated developments have made it possible to use the "turbo" system on almost any engine, be it gas, petrol or diesel. Moreover, the working cycle of the crankshaft (in two or four strokes) and the cooling method: with the help of air or liquid, do not play a role.
In addition to trucks and cars with engine power exceeding 80 kW, the system has found application in diesel locomotive, road construction equipment and marine engines with an increased working volume of 150 kW.
The principle of operation of an automobile turbine
The essence of the turbocharger is to increase the performance of a low-power engine with a minimum number of cylinders and a small amount of fuel by recycling the exhaust gases. The results can be amazing: for example, the liter three-cylinder engine is capable of delivering 90 horsepower without additional fuel, and with an indicator of high environmental friendliness.

The system works very simply: spent fuel - gases - does not immediately escape into the atmosphere, but enters the rotor of a turbine attached to the exhaust pipe, which, in turn, is on the same axis with the air blower. The hot gas spins the blades of the turbo system, and they set the shaft in motion, which contributes to the flow of air into the cold volute. The air compressed by the wheel, entering the unit, acts on the engine torque and under pressure, increasing the volume of gas-fuel liquid, contributes to an increase in the unit's power.
It turns out that for the effective operation of the engine, you need not more gasoline, but a sufficient amount of compacted air (which is completely free), which, when mixed with fuel, increases its efficiency (efficiency).
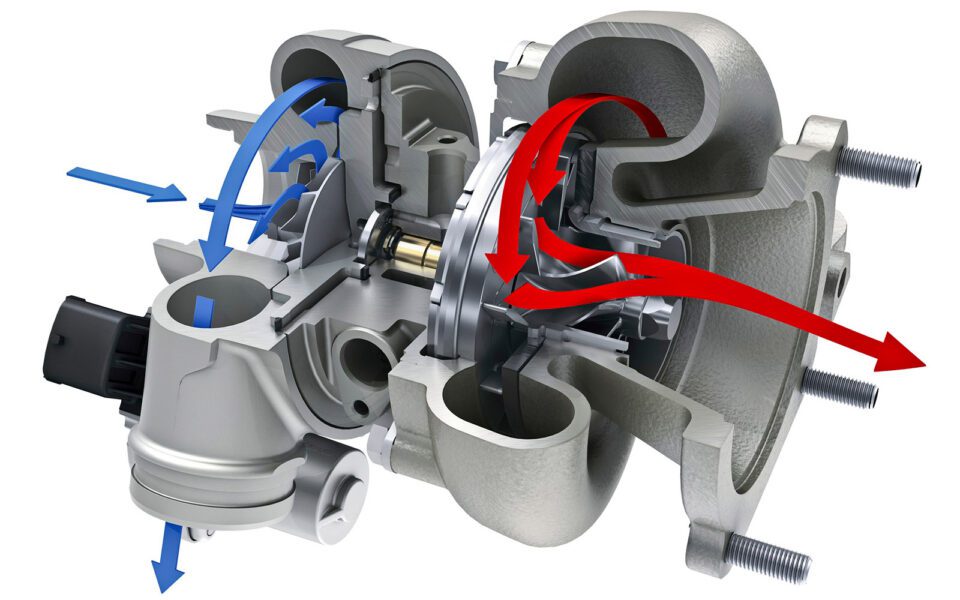
Turbocharger design
The energy converter is a mechanism consisting of two components: a turbine and a compressor, which play an equally important role in increasing the engine power of any machine. Both devices are located on one rigid axis (shaft), which together with the blades (wheels) forms two identical rotors: a turbine and a compressor, placed in housings that look like snails.

Schematic structure:
· Hot turbine volute (body). It takes over the exhaust gases that drive the rotor. For manufacturing, spheroidal cast iron is used, withstands strong heating.
· Impeller (wheel) of the turbine, rigidly fixed on a common axis. Usually leveled to prevent corrosion.
· Center cartridge housing with bearings between the rotor wheels.
· Cold compressor volute (body). After unwinding the shaft, the spent fuel (gases) draws in an additional volume of air. It is often made of aluminum.
· A compressor impeller (wheel) that compresses air and supplies it to the intake system under high pressure.
· Oil supply and drain channels for partial cooling of parts, prevention of LSPI (pre-low speed ignition), reduction of fuel consumption.
The design helps to use the kinetic energy from the exhaust gases to increase engine power without additional fuel consumption.
Turbine (turbocharger) functions
The turbo system is based on an increase in torque, which helps to increase the efficiency of the machine's motor. Moreover, the use of the device is not limited only to passenger and cargo vehicles. Currently, turbochargers with wheel sizes ranging from 220 mm to 500 mm are used on many industrial machines, ships, and diesel locomotives. This is due to some of the benefits that the technique gains:
· Turbo-device, subject to correct operation, will help to maximize the use of engine power in a stable mode;
· Productive work of the engine will pay off within six months;
· Installation of a special unit will save money on the purchase of a dimensional engine that "eats" more fuel;
· Fuel consumption becomes more rational with a constant volume of the engine;
· The efficiency of the engine almost doubles.
And what is important - the exhaust gases after secondary use becomes much cleaner, which means that it does not have such a detrimental effect on the environment.
Types and characteristics of the turbocharger
The unit installed on gasoline structures - separate - is equipped with two snails, which helps to preserve kinetic energy from exhaust gases and prevents them from re-entering the engine. The gasoline design requires a cooling chamber that lowers the temperature of the injected mixture (up to 1050 degrees) in order to avoid sudden premature ignition.

For diesel engines, cooling is generally not required, temperature and air pressure control is provided by nozzle devices that change geometry due to movable blades that can change the angle of inclination. The bypass valve with pneumatic or electric drive in diesel engines of medium power (50-130 HP) adjusts the settings of the turbocharger. And more powerful mechanisms (from 130 to 350 hp) are equipped with a device that regulates smooth (in two stages) fuel injection in strict accordance with the volume of air entering the cylinders.
All turbochargers are classified according to many basic characteristics:
· By the value of increasing efficiency;
· Maximum working temperature of exhaust gases;
· Torque of the turbine rotor;
· The difference in pressure of the forced air at the inlet and outlet from the system;
· On the principle of the internal device (change in the geometry of the nozzle or double design);
· By type of work: axial (feed along the shaft to the center and output from the periphery) or radial (action in reverse order);
· By groups, divided into diesel, gas, gasoline engines, as well as the horsepower of the units;
· On a one-stage or two-stage pressurization system.
Depending on the listed qualities, turbochargers can have a significant difference in size, additional equipment and be installed in different ways.
What is turbo lag (turbo pit)?
Effective turbocharger operation starts at an average vehicle speed, because at low speeds the unit does not receive enough exhaust gas to provide high rotor torque.
When the car starts abruptly from a standstill, exactly the same phenomenon is observed: the car cannot take instant acceleration, since the engine initially lacks the necessary air pressure. It should take some time to create medium-high revs, usually a few seconds. It is at this moment that the start delay occurs, the so-called turbo pit or turbo lag.
To solve this problem, modern vehicle models are equipped with not one, but two or three turbines operating in different modes. The turbo pits are also successfully dealt with by moving blades that change the geometry of the nozzle. Adjusting the angle of inclination of the wheel blades is able to create the required pressure in the engine.
What is the difference between a turbocharger and a turbocharger (turbocharging)?
The function of the turbine is to generate the torque of the rotor, which has a common axle with the compressor wheel. And the latter, in turn, creates an increased air pressure required for productive combustion of the fuel mixture. Despite the similarity of designs, both mechanisms have some significant differences:
· Installation of a turbocharger requires special conditions and skills, so it is installed either at the factory or in a specialized service. Any driver can install the compressor by himself.
· The cost of the turbo system is much higher.
· Compressor maintenance is easier and cheaper.
· Turbines are often used on more powerful engines, while a compressor with a small displacement is sufficient.
· The turbo system constantly requires oil to cool overheated parts. The compressor does not need oil.
· The turbocharger contributes to economical fuel consumption, while the compressor, on the contrary, increases its consumption.
· The turbo runs on pure mechanics, while the compressor needs power.
· When the compressor is running, there is no "turbo lag" phenomenon, the drive (unit) operation delay is observed only in the turbo.
· Turbocharging is activated by the exhaust gases, and the compressor is activated by the rotation of the crankshaft.
It cannot be said which system is better or worse, it depends on what kind of driving the driver is used to: for an aggressive one, a more powerful device will do; for a quiet one - a conventional compressor is enough, although now they are practically not produced in a separate form.
Turbocharger service life
The first power augmentation devices were notable for frequent breakdowns and did not have the most reliable reputation. Now the situation has improved a lot, thanks to modern innovative design developments, the use of heat-resistant materials for the body, the emergence of new types of oil, which requires particularly careful selection.
At present, the operational life of an additional unit can continue until the motor has exhausted its resources. The main thing is to pass technical inspections on time, which will help identify the slightest malfunctions at the initial stage. This will significantly save time for minor troubleshooting and money for repairs.
A timely and systematic change of the air filter and engine oil positively affects the smooth operation of the system and the extension of its life.
Operation and maintenance of automotive turbines
By itself, the power boost unit does not need separate maintenance, but its serviceability directly depends on the current state of the engine. The appearance of the first problems is indicated by:
· The appearance of extraneous noise;
· Noticeable consumption of engine oil;
• bluish or even black smoke coming out of the nozzle;
· A sharp decrease in engine power.
Often, side effects are directly related to the use of low-quality oil or its constant lack. In order not to worry about the untimely failure of the "main organ" and its "stimulator", you should follow the expert's advice:
· Clean the muffler, filter and check the catalyst condition in time;
· Constantly maintain the required oil level;
· Regularly check the condition of the sealed connections;
· Warm up the engine before starting operation;
· After aggressive driving for 3-4 minutes use idle speed to cool the turbine;
· Adhere to the manufacturer's recommendations for the use of a suitable filter and oil grade;
· Regularly undergo maintenance and monitor the condition of the fuel system.
If, nevertheless, the question of serious repairs arises, then it should be carried out only in a specialized workshop. The service must have ideal conditions for maintaining cleanliness, since the ingress of dust into the system is unacceptable. In addition, specific equipment is required for repair.
How to extend the life of a turbocharger?
Three main points ensure accurate and long-term operation of the turbine:
1. Timely replacement of the air filter and maintaining the required amount of oil in the engine. Moreover, you should use only those materials recommended by the manufacturer. You can buy original products from authorized dealers / representatives of the company, in order to avoid buying fakes.
2. An abrupt stop after a high-speed drive makes the system work without lubrication, since the turbine wheel continues to spin by inertia, and oil from the turned off engine no longer flows. This does not last long, about half a minute, but this constant practice leads to rapid wear of the ball bearing complex. So you need to either gradually reduce the speed, or let the engine run a little idle.
3. Do not put pressure on the gas suddenly. It is better to gain speed gradually so that the engine oil has time to properly lubricate the rotating mechanism.
The rules are very simple, but following them along with the manufacturer's recommendations will significantly extend the life of the car. As statistics show, only about 30% of drivers adhere to useful tips, therefore there are quite a few complaints about the inefficiency of the device.
What can break down in a car's turbocharger?
The most common breakdowns are associated with poor-quality engine oil and a clogged air filter.
In the first case, it is recommended to timely replace the contaminated part, and not to clean it. Such "savings" can lead to debris entering the middle of the system, which will adversely affect the quality of bearing lubrication.
Oil of dubious production has the same effect. Poor lubrication leads to rapid wear of internal parts, and not only the additional unit, but also the entire engine may suffer.
If the first signs of a malfunction are detected: the appearance of a lubricant leak, unwanted vibration, suspiciously loud sounds - you should immediately contact the service for a complete diagnosis of the motor.
Is it possible to repair a turbine in a car
The purchase of each new thing, and even more so related to mechanisms, is accompanied by the issuance of a warranty card, in which the manufacturer declares a certain period of the device's trouble-free service. But drivers in reviews often share their disappointments related to the discrepancy between the declared warranty period. Most likely, the fault lies not with the manufacturer, but with the owner himself, who simply did not adhere to the recommended operating rules.
If earlier the breakdown of the turbine meant the cost of a new device, then at the moment the unit is subject to partial restoration. The main thing is to turn to professionals in time with the proper equipment and certified original components. In no case should you do the repair yourself, otherwise you will not have to change a couple of parts, but the entire motor, and this will already cost much more.
Questions and answers:
What is the difference between a turbine and a turbocharger? These mechanisms have a different type of drive. The turbine is spun up by the flow of exhaust gases. The compressor is directly connected to the motor shaft.
How does a turbocharger work? The turbocharger drive is activated immediately when the engine is started, due to which the boost force is directly dependent on the engine speed. The impeller is capable of overcoming high drag.
What is the difference between a turbocharger and a turbocharger? Turbocharging is nothing more than a conventional turbine powered by the force of the exhaust stream. A turbocharger is a turbocharger. While it is easier to install, it is more expensive.
What is a turbocharger for? This mechanism, like a classic turbine, uses the energy of the motor itself (only in this case, the kinetic energy of the shaft, and not the exhaust gases) to enhance the flow of incoming fresh air.