
What is a manometer and what is it for
Content
- What is a manometer?
- What does he show and what measures?
- What does it consist of?
- Operating principle
- Types of manometers
- Benefits of using gauges
- What should be considered when choosing a pressure gauge?
- Conversion of pressure units of manometers
- What do you need to know to install pressure gauges?
- Features of operation of pressure gauges
- How is the calibration of manometers carried out
- Related videos
- Questions and answers:
What is a manometer?
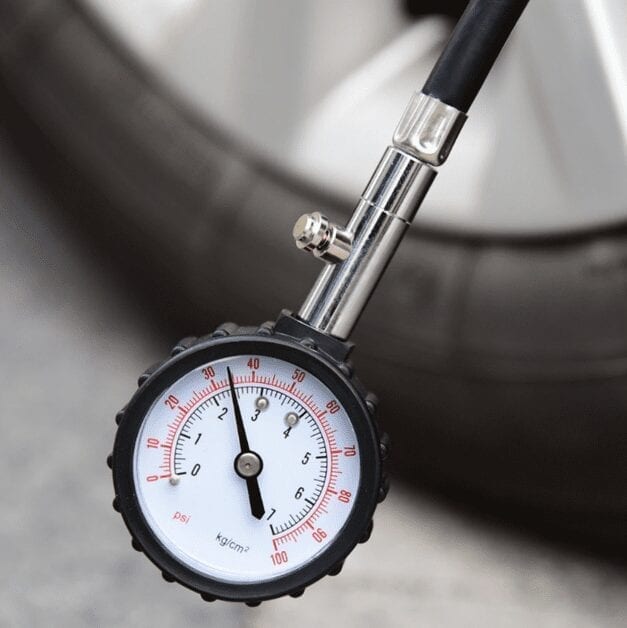
Automobile pressure gauge - a device for measuring pressure in automobile tires. In special equipment, pressure gauges are regularly used as a measurement of oil pressure and brake cylinders. Let's take a closer look at tire pressure gauges.
During the operation of vehicle tires, they lose pressure for various reasons, which leads to a deterioration in driving performance and danger when driving. It is impossible to determine the difference in pressure between the tires “by eye”, therefore we need a pressure gauge for accurate measurement.
What does he show and what measures?
An automobile pressure gauge is a device that shows the density of air inside a tire. The unit is kgf / cm² or Bar. Also, the measuring device can be used to measure the pressure in the air suspension cylinders. Ready-made sets of pneuma are often equipped with pointer devices from the KamAZ car, since it has a mechanical pointer device, showing pressure up to 10 atmospheres, and characterized by accuracy of indicators. The principle of operation of the manometer for tires and air suspension is the same, since they work according to a single principle.
What is a manometer for? First of all, for security. In previous articles, we touched on the topic of tire pressure differences, and what this leads to (uneven tire wear, increased risk of movement, increased fuel consumption). Often the device is integrated into the pump, whether mechanical or electric, but to read the tire pressure, the pump must be securely fixed to the valve, which is completely inconvenient.
What does it consist of?
The simplest mechanical pressure gauge consists of:
- housing;
- bourdon tubes or membranes;
- arrows;
- tubes;
- fitting.
Operating principle

The simplest mechanical pressure gauge works as follows: the main part is the Bourdon tube, which, when air pressure is injected, moves the arrow. When connected to a valve, air pressure acts on the brass tube, which tends to unbend, due to which the other end of the tube acts on the rod, moving the arrow. A similar principle of operation applies to the diaphragm pressure gauge.
An electronic pressure gauge is more complex, a sensitive element is used as a meter, the readings of which are transmitted to the electronic board, then to the display.
Types of manometers
Today there are three types of automobile pressure gauges:
- mechanical;
- rack-and-pinion;
- digital.
Mechanical. The peculiarity of such pressure gauges is their simple design and reliability. The cost of the device is low, relative to rack and digital devices. The main advantage is an instant and accurate reading of pressure, the availability of the device (sold in every auto shop), as well as reliability. The only drawback is the sensitivity to moisture.
Some mechanical pressure gauges not only show pressure, but also allow the release of excess air to achieve the required performance. For this, a pressure release button is located on the pressure gauge tube.
It is recommended to purchase more expensive models with a metal case, which differ in clear and correct indicators.
Rack and pinion. The body can be plastic or metal, the fitting is integrated into the body or there is a flexible hose of about 30 cm. The principle of operation is similar to a mechanical pressure gauge, the cost is as low, but the body is often prone to damage.

Digital. It is convenient in that it shows the pressure value up to hundredths. It is distinguished by clearer readings, there is a backlight display, however, in winter, the device may give values with errors. The electronic pressure gauge is the most compact, but the plastic case requires accuracy of use, otherwise there is a risk of crushing the case.
Depending on the area of application
Standard engineering pressure gauges are used to measure the pressure of non-crystallizing liquids, gases and steam. A key factor allowing the use of these types of gauges is contact with non-aggressive media.
For aggressive or special liquids / gases, special technical manometers are used. Such equipment is also used if the operating conditions are characterized by their instability, for example, constant strong vibrations, extremely high or low temperatures, etc.
Special devices include:
- Ammonia manometer;
- Corrosion resistant pressure gauge;
- Copper vibration-resistant pressure gauge;
- Vibration resistant stainless steel pressure gauge;
- Pressure gauge for accurate measurement;
- Railway pressure gauge;
- Electrocontact pressure gauge.
The first two types of devices are made of stainless steel or metal alloys that are resistant to aggressive environments. The following two types of instruments are installed to measure pressure in conditions with a vibration level higher than the normal parameter (which a standard pressure gauge can handle) by 4-5 times. In such pressure gauges, a special damping element is installed.
The presence of this element reduces the pulsation in the pressure gauge. In some vibration-resistant models, a special damping fluid is used (most often it is glycerin - it absorbs vibrations well).
The fifth category of devices is used in companies of state metrological control, heat, water, energy supply, at machine-building enterprises and other companies where the most accurate measurement of the pressure indicator is required. These instruments can be used as standards for calibration or verification of various equipment.
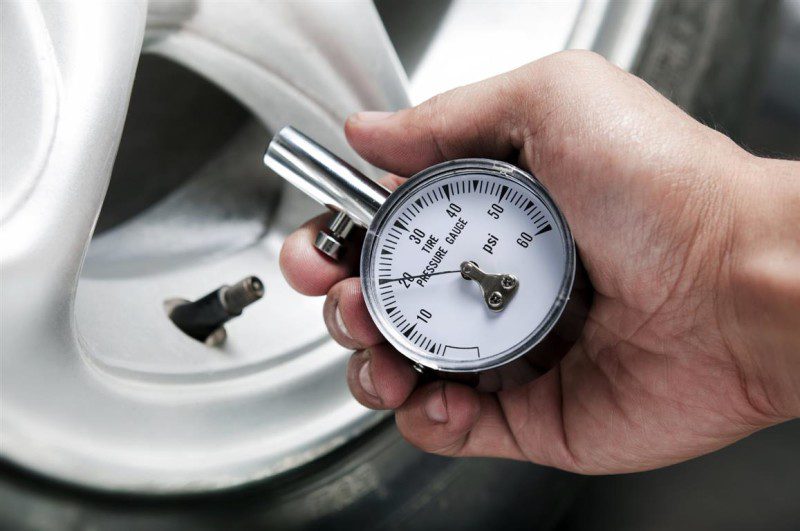

The railway pressure gauge is used in refrigeration systems, railway trains to measure excess vacuum. A feature of these devices is their vulnerability to substances aggressive to copper parts.
A feature of electrocontact manometers is the presence of an electrocontact group. Such devices are installed to measure pressure indicators of a non-aggressive medium and to automatically turn on / off the injection unit. An example of such pressure gauges is the design of a water supply station. When the pressure is below the set parameter, the pump turns on, and when the pressure reaches a certain threshold, the contact group opens.
Liquid pressure gauge: principle of operation
This type of pressure gauge works on the principle of the experience of Torricelli (one of the students of Galileo Galilei), and appeared in the distant XNUMXth century. Although this principle was described by Leonardo da Vinci in his treatise on hydraulics, his works became available only in the XNUMXth century. The artist described a method for measuring water pressure using the same system from a hollow U-shaped structure. In its modern design, the device consists of two tubes interconnected according to the principle of communicating vessels (U-shaped design).
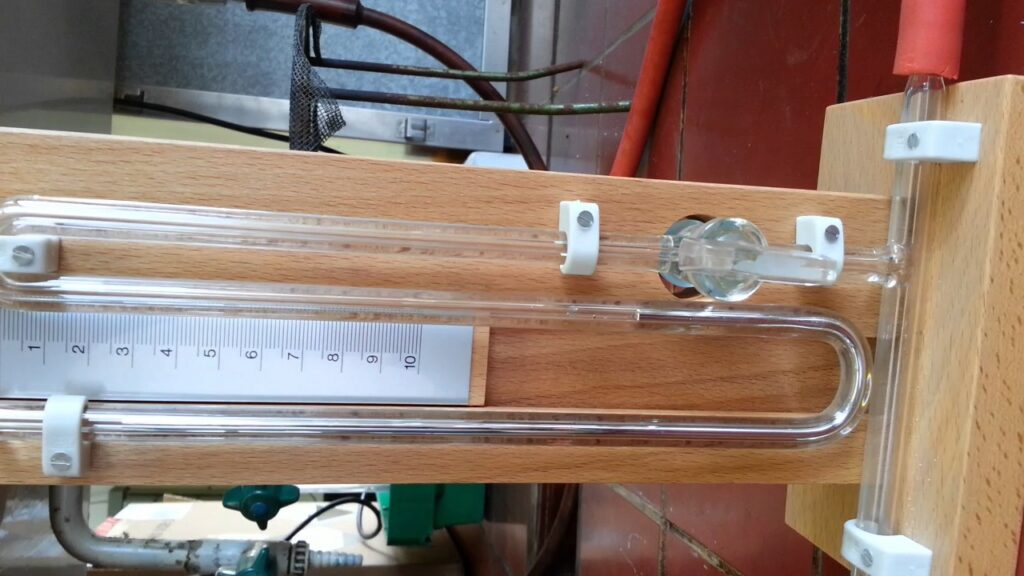
The tubes are half filled with liquid (usually mercury). When the liquid is exposed to atmospheric pressure, the liquid level in both tubes is the same. To measure the pressure in a closed system, an inflation circuit is connected to one of the tubes. If the pressure in the system is higher than atmospheric, the liquid level in one tube will be lower, and in the other - higher.
The difference in the height of the liquid is indicated in millimeters of mercury. To calculate how much it is in pascals, you need to remember: one centimeter of a mercury column is 1333.22 Pa.
Deformation gauges: principle of operation
Such devices immediately measure the pressure in pascals. The key element of the strain gauge is the spiral-shaped Bourdon tube. She's pumped up with gas. When the pressure in the tube increases, its turns are straightened. At the other end, it is connected to an arrow indicating the corresponding parameter on the graduated scale.
Instead of this tube, any elastic element can be used that can repeatedly deform and return to its original position when the pressure is released. It can be a spring, a diaphragm, etc. The principle is the same: the flexible element deforms under the action of pressure, and the arrow fixed at the end of the element indicates the pressure parameter.

Most often, both in domestic conditions and in production, it is precisely deformation manometers that are used. They differ from each other in the rigidity of the deforming element (depending on the measured pressure). This type of pressure gauge is used for cars.
Piston gauges: principle of operation
These are more rare gauges, although they appeared before the deformation counterparts. They are used in the oil and gas industry for well testing. The design of such pressure gauges can be different. The simplest option is a hollow container filled with oil and connected to the measured medium through a nipple.
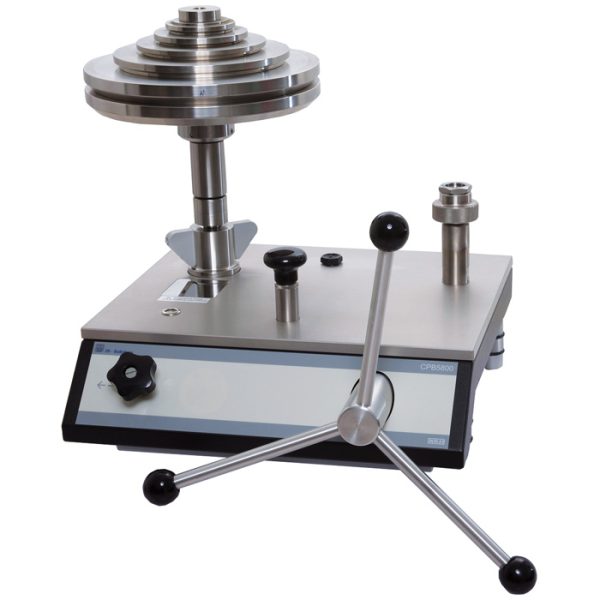

Inside this container there is a piston that fits snugly against the walls of the cavity along the entire perimeter. On top of the piston there is a platform (plate) on which the load is placed. Depending on the pressure to be measured, a suitable weight is selected.
Color marking
To prevent accidental installation of an unsuitable pressure gauge, the body of each type is painted in the corresponding color. For example, to work with ammonia, the pressure gauge will be colored yellow, with hydrogen - in dark green, with flammable gases - in red, with oxygen - in blue, with non-combustible gases - in black. The pressure gauge in contact with chlorine will have a gray housing, with acetylene - white.
In addition to the color coding, special pressure gauges are additionally marked with the measurement medium. For example, in oxygen pressure gauges, in addition to the blue color of the case, the inscription O2 will also be present.
Benefits of using gauges
What is a manometer for? First of all, it is an indispensable assistant for every car enthusiast, especially for those who often use the vehicle to move on sand and off-road, where pressure relief or pumping is required.
How to use a manometer? Quite simply: you need to insert the fitting into the tire valve, after which the arrow of the device will show the real pressure. The digital device must first be turned on. By the way, in order not to constantly check tire inflation, there are special valves with pressure sensors. The simplest sensors are equipped with nipples with three-color divisions: green - pressure is normal, yellow - requires pumping, red - the wheel is flat.
There are also ready-made systems with an LCD display that is installed in the cabin, notifying 24/7 about the status of tire pressure. Most modern cars are already equipped with a standard tire pressure information system, and SUVs with a function of pumping or depressurizing. One way or another, having a pressure gauge with you is extremely important, since the correct tire pressure is the key to safe and comfortable driving.
What should be considered when choosing a pressure gauge?
Before purchasing new equipment, there are several important parameters to consider. This is not necessary if a specific modification is used for the application and is commercially available. It is necessary to take into account the special parameters if the original is not on sale, but its analogue is selected.
Measurement range parameter
Perhaps this is one of the most important parameters by which new pressure gauges are selected. The standard range of pressure gauges includes such values (kg / cm2):
- 0-1;
- 0-1.6;
- 0-2.5;
- 0-4;
- 0-6;
- 0-10;
- 0-16;
- 0-25;
- 0-40;
- 0-60;
- 0-100;
- 0-160;
- 0-250;
- 0-400;
- 0-600;
- 0-1000.

In one kg / cm20.9806 bar or 0.09806 MPa.
For manovacuum meters, the standard range of values (kgf / cm2):
- From -1 to +0.6;
- From -1 to +1.5;
- From -1 to +3;
- From -1 to +5;
- From -1 to +9;
- From -1 to +15;
- From -1 to + 24.
In one kgf / cm2 two atmospheres (or bar), 0.1 MPa.
For vacuum gauges, the standard range is -1 to 0 kilogram-force per square centimeter.
If there is any doubt about which scale should be on the device, it must be taken into account that the working pressure is between 1/3 and 2/3 of the scale. For example, if the measured pressure should be 5.5 atmospheres, then it is better to take a device that measures up to ten atmospheres at a maximum value.
If the measured pressure is less than 1/3 of the scale division, then the device will show inaccurate information. If a device is purchased, the maximum value of which is close to the measured pressure, then during measurements the pressure gauge will work under conditions of increased load and will quickly fail.
Accuracy class parameter
In other words, this is the parameter of the error that the manufacturer of a particular model of equipment allows. The standard list of accuracy classes includes models with the following parameters:
- 4;
- 2.5;
- 1.5;
- 1;
- 0.6;
- 0.4;
- 0.25;
- 0.15.
Naturally, the smaller the error of the device, the higher its cost. If the accuracy class specified by the manufacturer does not match, the device cannot be used, as it will show incorrect data. You can find out about this discrepancy as follows. For example, the maximum value on the scale is set at 10 atmospheres. The device has an error class of 1.5. that is, a 1.5% mismatch is acceptable. This means that the permissible deviation on the scale is possible (in this case) by 0.15 atm.

It is impossible to calibrate or check the device at home, as this requires a reference device with a minimum error. To check for serviceability, these pressure gauges are connected to one line. Pressure is supplied through it, and the indicators of the devices are compared.
Gauge diameter parameter
This characteristic is of great importance for models with a round body and a corresponding scale. The larger the diameter, the more marks can be made, and more accurate parameters can be determined.
The list of standard diameters (in millimeters) of gauges includes:
- 40;
- 50;
- 63;
- 80;
- 100;
- 150;
- 160;
- 250.
Choke location
The position of the test point is also important. There are models with:
- Radial arrangement. In this case, it is located at the bottom of the device under the scale. This makes it easy to measure pressure parameters in cavities that are difficult to access. Car wheels are an example of this;
- End location. In this case, the nipple is located on the back of the device.
The appropriate model is selected depending on the measurement conditions and the characteristics of the measuring points on the line or vessel. This is necessary so that the fitting fits as tightly as possible to the measuring hole of the container.
Connecting thread
Most of the pressure gauges are equipped with metric and pipe connecting threads. The following sizes are standard:
- M10 * 1;
- M12 * 1.5;
- M20 * 1.5;
- G1 / 8;
- G1 / 4;
- G1 / 2.

Domestic manometers are sold with a metric thread of the connecting pipe. Imported analogs - with pipe threads.
Calibration interval
This is the interval at which the equipment must be checked. When buying a new pressure gauge, it has already been verified (at the factory). This is indicated by the corresponding sticker. Such verification is required by professional equipment. If an option is purchased for domestic use, then such a procedure is not necessary.
Initial verification of equipment for departmental companies is valid for one or two years (depending on the specifics of the company). This procedure is carried out by licensed companies. Often you have to spend more money on rechecking than buying new equipment.
For this reason, if there is a need to use a calibrated pressure gauge, it is more practical to purchase an option with a two-year initial verification. When the time comes to perform a rechecking, you need to calculate how much this procedure will result in, including putting the device into operation and, if necessary, repairing it.

If in the system in which the pressure gauge is installed, water shocks often occurred or it was subjected to other high loads, then after two years of operation, half of the equipment does not pass verification, and you still need to pay for the procedure.
Operating conditions of pressure gauges
This is another factor that must be considered when choosing a new pressure gauge. In the case of operation under conditions with increased load due to exposure to viscous or aggressive substances, constant vibrations, as well as extreme temperatures (exceeding +100 and below -40 degrees), it is necessary to purchase specialized equipment. Typically, the manufacturer specifies the ability of the gauge to work under these conditions.
Conversion of pressure units of manometers
It is often necessary to measure non-standard pressure values. Non-standard scales are used on professional gauges, but they are more expensive. Here's how you can convert non-standard units of measurement into the metrics we are used to.
In one kgf / cm2 10000 kgf / m2, one atmosphere, one bar, 0.1MPa, 100 kPa, 100 Pa, 000 millimeters of water, 10 millimeters of mercury, or one thousand mbar. You can create the required scale with the corresponding symbols yourself.
What do you need to know to install pressure gauges?
To install a pressure gauge on a line under pressure, you need to use special equipment. In this case, a three-way valve is required as well as a needle valve. To protect the device, a diaphragm seal, a damper block and a loop selection element are installed.
Let's consider the features of each of these devices.
Three-way valve for pressure gauge
A ball or plug three-way valve is used to connect the pressure gauge to the line. In some cases, it is allowed to install a two-way analog, but it must necessarily have a manual reset. It all depends on the characteristics of the highway.
A conventional tap is not suitable, because even after closing off the medium access to the pressure gauge, the device remains under pressure (the pressure is inside the device). Because of this, it can quickly fail. A three-way plug or ball valve is used on lines with pressures up to 25 kilogram-force per square centimeter. If the pressure in the line is higher, then a pressure gauge should be installed through a needle valve.
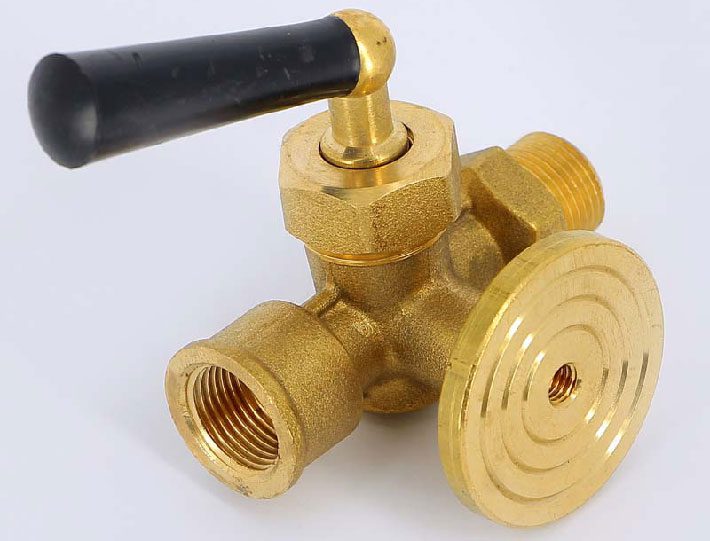

When purchasing a new gauge and valve, make sure that the threads are correct.
Damper block
As the name suggests, this device is designed to dampen pulsations inside a line (water hammer). The damper block is placed in front of the pressure gauge, taking into account the direction of movement of the medium. If you do not extinguish the resulting water hammer, this will affect the accuracy of the pressure measurement.
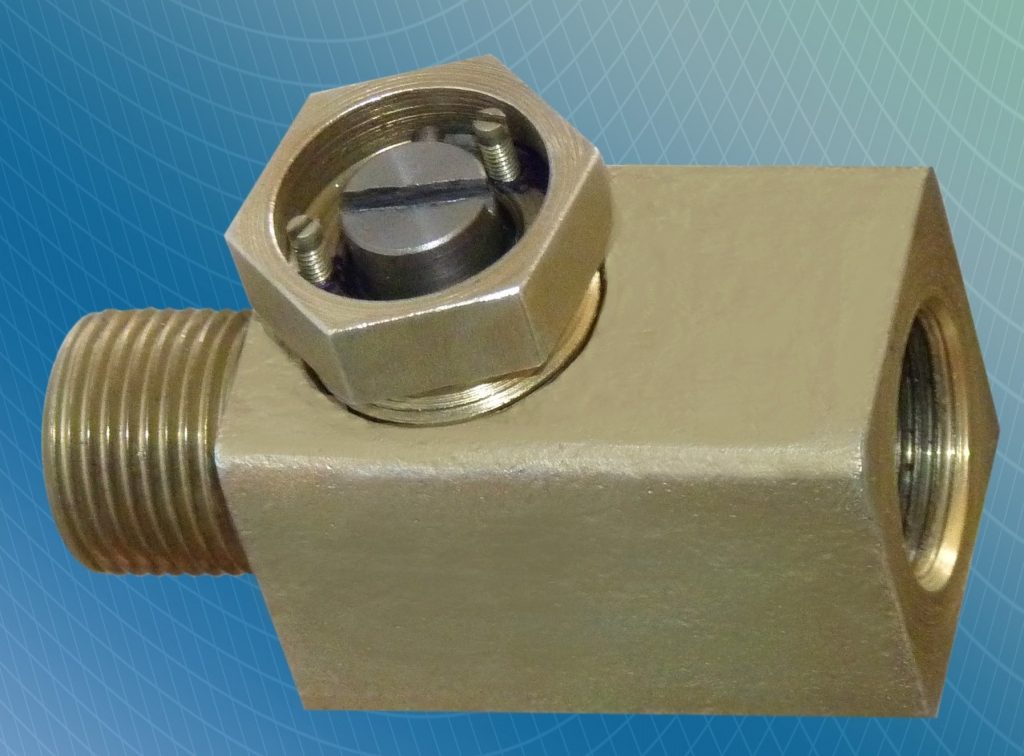

Ripple in the line may be due to the operation of a pump that is not equipped with a soft start. Also, water hammer occurs when opening / closing conventional ball valves. They abruptly cut off the outlet of the working medium, which is why there is a sharp jump in the pressure inside the line.
Diaphragm seals
The diaphragm seal prevents the mixing of two different substances that fill two different circuits in the system. A simple example of such elements is a membrane that is installed in the working areas of the Hydractive hydropneumatic suspension (see details about it in another review).
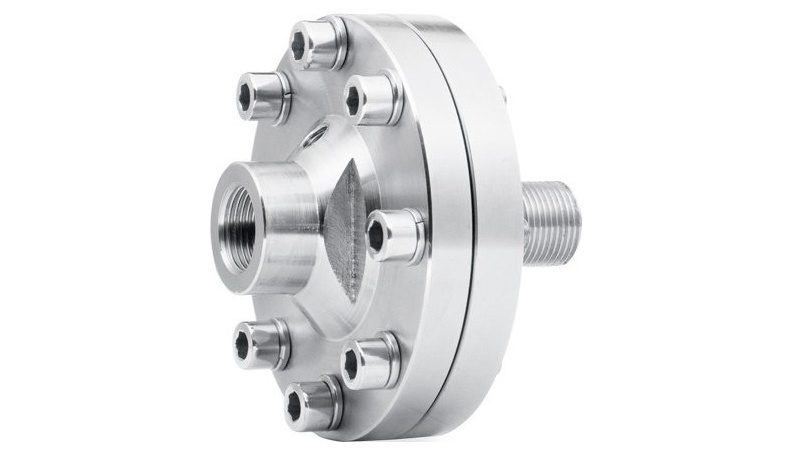

If an individual diaphragm seal is used in the line (a separate device that is not included in the device of certain mechanisms), then when connecting a pressure gauge to it, make sure that their threads match.
Needle valve block
This is a device with which the following are integrated into the backbone:
- Overpressure sensor;
- Absolute pressure sensor;
- Pressure-vacuum sensor;
- Pressure gauges.
This unit allows drainage of line impulses and discharge of pressure before performing installation work on the line. Thanks to this unit, it is possible, without disconnecting the sensors from the measured medium, to connect or replace the measuring equipment.
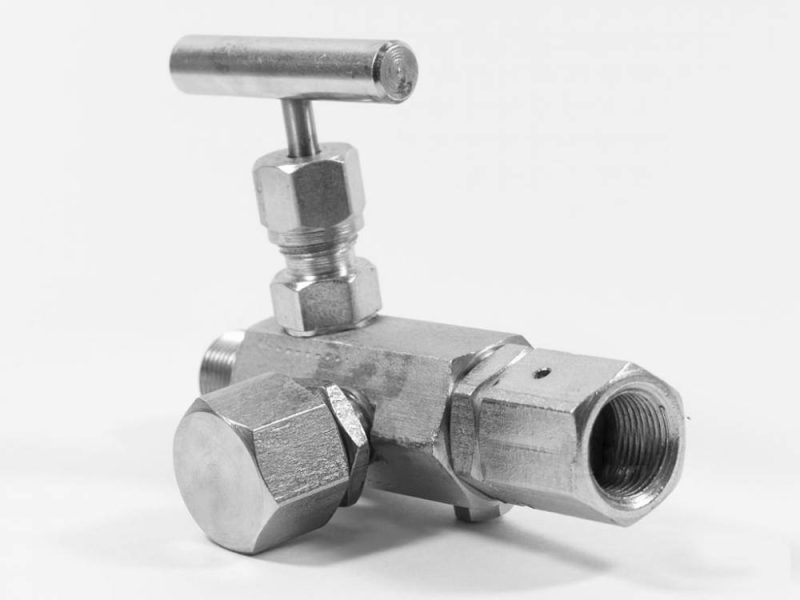

When installing a pressure gauge, the following points must be considered:
- Make sure that there is no pressure in the line;
- The scale of the device must be vertical;
- Do not twist the device by holding its dial. It is necessary to screw it into the line, holding the fitting with a wrench of the appropriate size;
- Do not apply force to the pressure gauge body.
Features of operation of pressure gauges
Since the operation of the pressure gauge is associated with high loads, improper operation of the device can significantly reduce its working life. First of all, it is necessary to follow the manufacturer's recommendations specified in the technical documentation of the device. Do not use pressure gauges that are not designed to measure the pressure of aggressive media or those that cannot withstand constant vibrations, critically high or low temperatures.
That is, when choosing a new device, it is necessary to take into account the conditions in which it will work. One of the most important factors affecting the correct operation of pressure gauges is a smooth supply of pressure. For this reason, cheap car gauges quickly fail. If the device is selected in accordance with the operating conditions, then it will work properly for the entire period assigned to it.
The operation of the pressure gauge is not allowed in the event of:
- With a smooth supply of pressure in the line, the arrow of the device is deflected in jerks or does not move at all, but moves only at maximum pressure;
- There is damage on the case, for example, glass cracked;
- When the pressure is released, the arrow of the device does not return to its original position;
- The manometer error does not correspond to the parameter declared by the manufacturer.
How is the calibration of manometers carried out
As we have already noted, there is a primary and repeated calibration of pressure gauges. The primary procedure is carried out at the manufacturing stage prior to its sale. Verification is usually valid for one to two years. This period will be indicated on a label stuck on the body of the device or in its passport.
After the expiration of this period, the device requires rechecking. In this case, it must be serviceable. If there are doubts about this, then it is better to buy a new pressure gauge, because funds for checking the health of an inoperative device are not returned.
At the end of the review, we offer TOP-5 pressure gauges of 2021:
Related videos
In conclusion - a short video lecture on the operation of pressure gauges:


Watch this video on YouTube
Questions and answers:
What are the units of measurement of the pressure gauge? All pressure gauges measure pressure in the following units: bar; kilogram-force per square centimeter; millimeters of water column; millimeters of mercury; meters of water column; technical atmospheres; newtons per square meter (pascals); megapascals; kilopascals.
How does a pressure gauge work? The pressure is measured by the action of the pressure on the elastic element of the device connected to the arrow. The elastic element is deformed, due to which the arrow deflects, indicating the corresponding value. To measure the pressure of a certain force, a device is required that can withstand a head three times the required value.
What does a pressure gauge consist of? This is a cylindrical device with a metal (less often plastic) body and a glass cover. A scale and an arrow are visible under the glass. On the side (in some models on the back) there is a threaded connection. Some models also have a pressure relief button on the body. It must be pressed every time after measuring the pressure (this is necessary so that the elastic element is not under constant pressure and does not deform). There is a mechanism inside the device, the main part of which is an elastic element connected to the arrow. Depending on the purpose of the device, the mechanism may differ from the simpler version.
One comment
anonym
in what order this device is used in manufacturing enterprises