What is a crankshaft in a car and how does it work
Content
- Crankshaft in car
- What is a crankshaft for?
- Crankshaft structure
- What is a crankshaft sensor for?
- Crankshaft shape
- How the crankshaft works in a car engine
- Possible crankshaft problems and their solutions
- Crankshaft service
- The crankshaft is removed in the following sequence:
- Repair and cost of a damaged crankshaft
- Algorithm for checking the crankshaft:
- Crankshaft grinding
- Related videos
- Questions and answers:
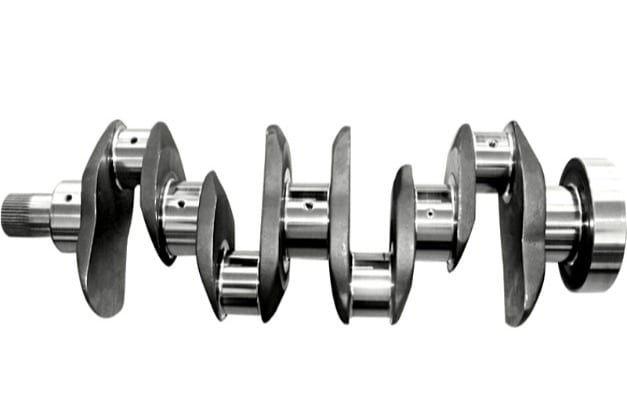
Crankshaft in car
A crankshaft is a part in a car’s motor driven by a piston group. It transfers torque to the flywheel, which in turn rotates the gears of the transmission. Further, the rotation is transmitted on the drive axles.
All cars under the hood of which are installed internal combustion engines, equipped with such a mechanism. This part is created specifically for the brand of the engine, and not for the car model. During operation, the crankshaft is rubbed against the structural features of the internal combustion engine in which it is installed. Therefore, when replacing it, minders always pay attention to the development of rubbing elements and why it appeared.
What does the crankshaft look like, where is it and what are the faults?
Crankshaft history
As a standalone product, the crankshaft did not appear overnight. In the beginning, the crank technology appeared, which was applied in various fields of agriculture, as well as in industry. For example, hand-operated cranks were used as early as 202-220 AD. (during the Han dynasty).
A distinctive feature of such products was the lack of a function for converting reciprocating movements into rotational or vice versa. Various products made in the shape of a crank were used in the Roman Empire (II-VI centuries AD). Some tribes of central and northern Spain (Celtiberians) used hinged hand mills, which worked on the principle of a crank.

In different nations, this technology has been improved and used in different devices. Many of them were used in wheel turning mechanisms. Around the 15th century, the textile industry began using crank drums onto which skeins of yarn were wound.
But the crank alone does not provide rotation. Therefore, it must be combined with another element that would provide the conversion of reciprocating movements into rotation. The Arab engineer Al-Jazari (lived from 1136 to 1206) invented a full-fledged crankshaft, which, with the help of connecting rods, was capable of performing such transformations. He used this mechanism in his machines to raise water.
On the basis of this device, various mechanisms were gradually developed. For example, a contemporary of Leonardo da Vinci, Cornelis Corneliszun, built a sawmill that was powered by a windmill. In it, the crankshaft will perform the opposite function compared to the crankshaft in the internal combustion engine. Under the influence of the wind, the shaft rotated, which, with the help of connecting rods and cranks, converted rotary movements into reciprocating movements and moved the saw.
As the industry developed, crankshafts gained more and more popularity due to their versatility. The most efficient engine to date is based on the conversion of reciprocating motion into rotational motion, which is possible thanks to the crankshaft.
What is a crankshaft for?
As you know, in most classic internal combustion engines (about how other internal combustion engines can work, read in another article) there is a process of converting reciprocating movements into rotational movement. Pistons with connecting rods are installed in the cylinder block. When a mixture of air and fuel enters the cylinder and is ignited by a spark, a lot of energy is released. Expanding gases push the piston towards bottom dead center.
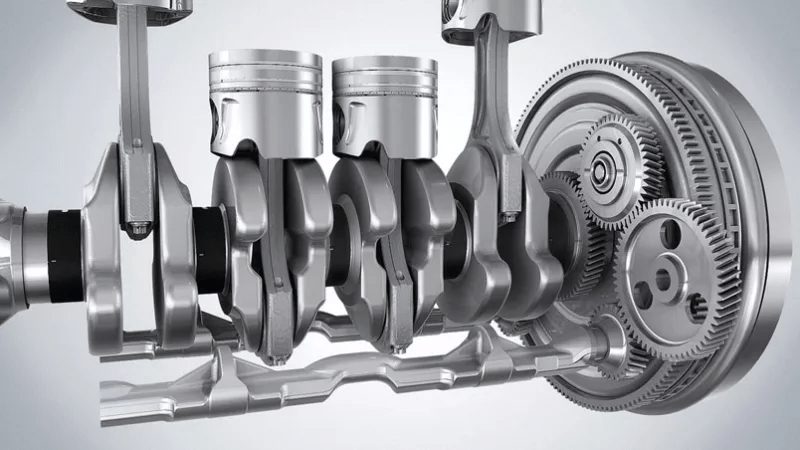

All cylinders are mounted on connecting rods, which in turn are attached to the crankshaft connecting rod journals. Due to the fact that the moment of actuation of all cylinders is different, a uniform effect is exerted on the crank mechanism (the vibration frequency depends on the number of cylinders in the motor). This causes the crankshaft to rotate continuously. The rotational motion is then transmitted to the flywheel, and from it through the clutch to the gearbox and then to the drive wheels.
So, the crankshaft is designed to convert all kinds of movements. This part is always created extremely accurately, since the cleanliness of rotation of the input shaft in the gearbox depends on the symmetry and precisely calibrated angle of inclination of the cranks relative to each other.
Materials from which the crankshaft is made
For the manufacture of crankshafts, steel or ductile iron is used. The reason is that the part is under heavy load (high torque). Therefore, this part must be of high strength and rigidity.
For the manufacture of cast iron modifications, casting is used, and steel modifications are forged. To give the ideal shape, lathes are used, which are controlled by electronic programs. After the product gets the desired shape, it is sanded, and to make it stronger, it is processed using high temperatures.
Crankshaft structure

The crankshaft is installed in the lower part of the engine directly above the oil sump and consists of:
- of the main neck - the supporting part of the part on which the main bearing of the crankcase is mounted;
- connecting rod neck - stops for connecting rods;
- cheeks - connect all connecting rod journals with the main ones;
- sock - the output part of the crankshaft, on which the timing belt drive pulley is mounted;
- shank - the opposite part of the shaft to which the flywheel is mounted, which drives the gears of the gearbox, and the starter is also connected to it;
- counterweights - serve to maintain balance during reciprocating movements of the piston group and relieve the load of centrifugal force.
The crankshaft axis is the main necks, and the connecting rods are always alternately shifted in the opposite direction from each other. In these elements, holes are made for supplying oil to the bearings.
The crankshaft crank is a unit consisting of two cheeks and one connecting rod neck.
Previously, prefabricated crank modifications were installed in cars. Today, all engines are equipped with integral crankshafts. They are made of high-strength steel by forging, and then processing on lathes. Less expensive options are made of cast iron by casting.
Here is an example of creating a steel crankshaft:
What is a crankshaft sensor for?
DPKV is a sensor that determines the position of the crankshaft at a certain moment. This sensor is always installed in vehicles with electronic ignition. Read more about electronic or contactless ignition here.
In order for the air-fuel mixture to be supplied to the cylinder at the right time, and also to ignite it on time, it is necessary to determine when each cylinder performs the appropriate stroke. The signals from the sensor are used in various electronic vehicle control systems. If this part does not work, the power unit will not be able to start.
There are three types of sensors:
- Inductive (magnetic). A magnetic field is formed around the sensor, into which the synchronization point falls. The timing tag allows the electronic control unit to send the desired pulses to the actuators.
- Hall Sensor. It has a similar principle of operation, only the magnetic field of the sensor is interrupted by a screen fixed to the shaft.
- Optic. A toothed disc is also used to synchronize the electronics and rotation of the crankshaft. Only instead of a magnetic field, a luminous flux is used, which falls on the receiver from the LED. The impulse going to the ECU is formed at the moment of interruption of the light flux.
For more information about the device, the principle of operation and malfunctions of the crankshaft position sensor, read in a separate review.
Crankshaft shape
The shape of the crankshaft depends on the number and location of the cylinders, their order of operation and the strokes that are performed by the cylinder-piston group. Depending on these factors, the crankshaft can be with a different number of connecting rod journals. There are motors in which the load from several connecting rods acts on one neck. An example of such units is a V-shaped internal combustion engine.
This part should be manufactured so that during rotation at high speeds vibration is minimized as much as possible. Counterweights can be used depending on the number of connecting rods and the order in which crankshaft flares are generated, but there are also modifications without these elements.
All crankshafts fall into two categories:
- Full support crankshafts. The number of main journals is increased by one in comparison with the connecting rod. This is due to the fact that on the sides of each crank pin there are supports, which also serve as the axis of the crank mechanism. These crankshafts are most commonly used because the manufacturer can use lightweight material, which affects engine efficiency.


- Non-full-support crankshafts. In such parts, there are fewer main journals than crank ones. Such parts are made of more durable metals so that they do not deform or break during rotation. However, this design increases the weight of the shaft itself. Basically, such crankshafts were used in low-speed engines of the last century.


The full-support modification proved to be lighter and more reliable, therefore it is used in modern internal combustion engines.
How the crankshaft works in a car engine
What is a crankshaft for? Without it, the movement of the machine is impossible. The part works on the principle of bicycle pedaling. Automotive engines alone use more connecting rods.
The crankshaft works as follows. The air-fuel mixture ignites in the engine cylinder. The generated energy pushes the piston. In this case, a connecting rod connected to the crankshaft crank is driven. This part makes a constant rotational movement around the axis of the crankshaft.


At this moment, another part located on the opposite side of the axis moves in the opposite direction and lowers the next piston into the cylinder. The cyclical movement of these elements leads to smooth rotation of the crankshaft.
So the reciprocating movement is converted into rotational. Torque is transmitted to the timing pulley. The operation of all engine mechanisms - a water pump, an oil pump, a generator and other attachments - depends on the rotation of the crankshaft.
Depending on the engine modification, cranks can be counted from one to 12 (one per cylinder).
For details on the principle of operation of the crank mechanism and the types of modifications, see the video:


Watch this video on YouTube
Possible crankshaft problems and their solutions
Although the crankshaft is made of durable metal, it can fail due to constant loads. This part experiences mechanical stress from the piston group (sometimes the pressure on one crank can reach ten tons). In addition, while the motor is running, the temperature inside it rises to several hundred degrees.
Here are some of the causes of breakdowns of the component of the crank mechanism.
Crank pin crank journals


The wear of the connecting rod journals is a common malfunction, since friction force is generated in this assembly under high pressure. As a result of such loads on the metal, workings appear that impede the free movement of the bearings. Because of this, the crankshaft is heated unevenly and can subsequently become deformed.
Ignoring this problem is fraught not only with strong vibrations in the motor. Overheating of the mechanism leads to its destruction and through a chain reaction - the entire engine.
The problem is eliminated by grinding the connecting rod journals. Moreover, their diameter decreases. In order for the size of these elements to be the same on all cranks, this procedure should be performed exclusively on professional turning machines.


Since after the procedure the technical clearances of the part become larger, after processing a special insert is installed on them to compensate for the formed space.
Scuffing occurs due to low oil in the crankcase. The occurrence of a malfunction is also affected by the quality of the lubricant. If you do not change the oil on time, it thickens, which makes the oil pump unable to create the necessary pressure in the system. Timely maintenance will allow the crank mechanism to work for a long time.
Crank Dowel Slice


The key of the crank mechanism allows you to transfer torque from the shaft to the drive pulley. These two elements are equipped with grooves into which a special wedge is inserted. Due to low-quality material and heavy load, this part can be cut off in rare cases (for example, when the engine is jammed).
If the grooves of the pulley and the crankshaft are not broken, then simply replace this key. In older engines, this procedure may not bring the desired result due to backlash on the joint. Therefore, the only way out of the situation is to replace these parts with new ones.
Flange hole wear


A flange with several holes for connecting the flywheel is fixed on the shank of the crankshaft. Over time, these nests may break. Such malfunctions are classified as fatigue wear.
As a result of the mechanism working under heavy loads, microcracks form in the metal parts, due to which single or group depressions form on the joints.
The malfunction is eliminated by drilling holes for a larger diameter bolts. This manipulation should be performed with both the flange and the flywheel.
Stuffing box leak


Two oil seals are installed on the main shaft necks (one on each side). They prevent oil from escaping from under the main bearings. If grease gets on timing belts, this significantly reduces their service life.
Oil seal leakage may occur for the following reasons.
- Vibrations of the crankshaft. In this case, the inner part of the gland wears out, and it does not fit snugly against the neck.
- Long downtime in the cold. If the car stands on the street for a long time, the oil seal dries up and loses its elasticity. And because of the frost, he is dubbing.
- The quality of the material. Budget details always have a low working resource.
- Installation error. Most mechanics install using a hammer, carefully stuffing an oil seal on the shaft. For the part to function longer, the manufacturer recommends using the tool designed for this procedure (mandrel for bearings and seals).
Most often, oil seals wear out at the same time. However, if there is a need to replace only one, the second should be changed.
Crankshaft Sensor Malfunction


This electromagnetic sensor is mounted on the engine to synchronize the operation of the injector and ignition systems. If it is faulty, then the motor cannot be started.
The crankshaft sensor detects the position of the cranks at the dead center of the first cylinder. Based on this parameter, the vehicle’s electronic control unit determines the moment of fuel injection into each cylinder and spark supply. Until a pulse is received from the sensor, a spark will not form.
If this sensor fails, the problem is solved by replacing it. Just choose the model that is designed for this type of engine, otherwise the parameters of the crankshaft position will not correspond to reality, and the internal combustion engine will not function properly.
Crankshaft service
There are no parts in the car that do not need periodic inspection, maintenance or replacement. The same goes for crankshafts. Since this part is constantly under heavy load, it wears out (this happens especially quickly if the motor often experiences oil starvation).
To check the condition of the crankshaft, it must be removed from the block.
The crankshaft is removed in the following sequence:
- First you need to drain the oil;
- Next, you need to remove the motor from the car, then all its elements are disconnected from it;
- The internal combustion engine body is turned upside down with the pallet;
- In the process of disassembling the crankshaft mount, it is necessary to remember the location of the main bearing caps - they are different;
- The covers of the support or main bearings are dismantled;
- The rear o-ring is removed and the part is removed from the body;
- All main bearings are removed.
Next, we check the crankshaft - in what condition it is.
Repair and cost of a damaged crankshaft
The crankshaft is an extremely difficult part to repair. The reason is that this part operates at high rpm under heavy loads. Therefore, this part must have perfect geometry. This can only be achieved using high-precision equipment.
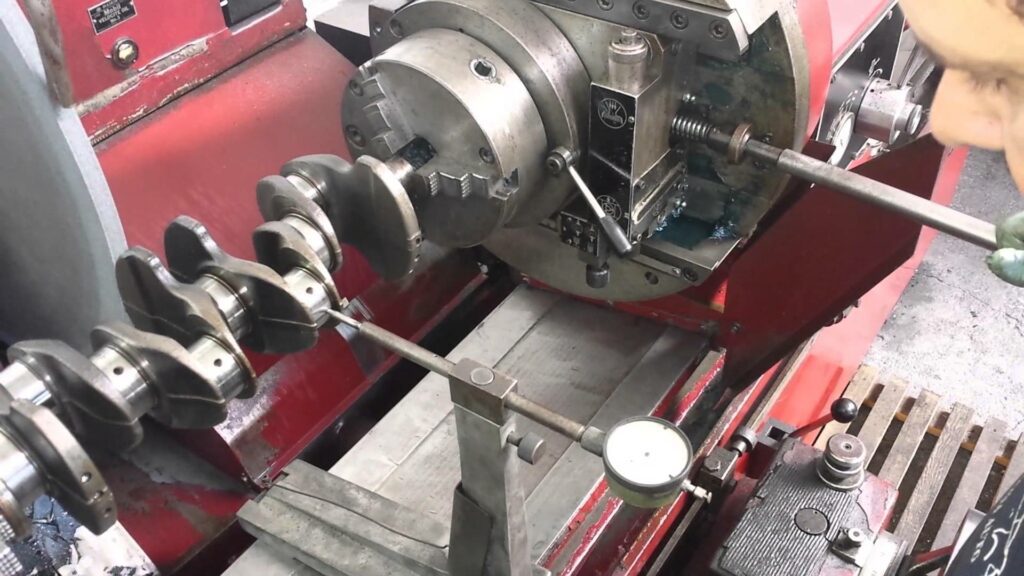


If the crankshaft needs to be ground due to the appearance of scoring and other damage, this work must be performed by a professional technician using special equipment. To restore a worn crankshaft, in addition to grinding, it needs:
- Cleaning of channels;
- Replacement of bearings;
- Heat treatment;
- Balancing.
Naturally, such work can only be performed by highly qualified specialists, and they will take a lot of money for this (the work is performed on expensive equipment). But this is just the tip of the iceberg. Before the master starts repairing the crankshaft, it must be removed from the engine, and then correctly installed in place. And this is additional waste on the work of a minder.
The cost of all these works depends on the price of the master. This needs to be clarified in the area where such work is being carried out.
It makes no sense to repair only the crankshaft when fully disassembling the engine, so it is better to immediately combine this procedure with the overhaul of the internal combustion engine. In some cases, it is easier to buy a contract motor (imported from another country not under the hood of a car and without a run through the territory of this country) and install it instead of the old one.
Algorithm for checking the crankshaft:
To determine the condition of a part, it must be flushed with gasoline to remove residual oil from the surface and from the oil channels. After flushing, the part is flushed with a compressor.
Further, the check is carried out in the following sequence:
- An inspection of the part is carried out: there are no chips, scratches or cracks on it, and it is also determined how much it is worn out.
- All oil passages are purged and purged to identify possible blockages.
- If scuffs and scratches are found on the connecting rod journals, the part is subject to grinding and subsequent polishing.
- If damage is found on the main bearings, they must be replaced with new ones.
- A visual inspection of the flywheel is carried out. If it has mechanical damage, the part is changed.
- The bearing mounted on the toe is examined. In case of defects, the part is pressed out, and a new one is pressed in.
- The oil seal of the camshaft cover is checked. If the car has a high mileage, then the oil seal must be replaced.
- The seal on the rear of the crankshaft is being replaced.
- All rubber seals are checked and, if necessary, replaced.
After inspection and proper maintenance, the part is returned to its place and the motor is assembled in the reverse order. After completing the procedure, the crankshaft should rotate smoothly, without much effort or jerking.
Crankshaft grinding
Regardless of what material the crankshaft is made of, sooner or later a working out is formed on it. At the earliest stages of wear, to extend the working life of a part, it is ground. Since the crankshaft is a part that must be perfectly shaped, the grinding and polishing process must be carried out by an understanding and experienced turner.
He will do all the work on his own. Only the purchase of repair connecting rod bearings (they are thicker than the factory ones) depends on the car owner. The repair parts differ in their thickness, and there are sizes 1,2 and 3. Depending on how many times the crankshaft has been ground or on the degree of its wear, the corresponding parts are purchased.
For more information about the function of the DPKV and the diagnosis of its malfunctions, see the video:


Watch this video on YouTube
Related videos
Additionally, watch a video on how the crankshaft is restored:


Watch this video on YouTube
Questions and answers:
Where is the crankshaft? This part is located in the engine housing under the cylinder block. Connecting rods with pistons on the opposite side are attached to the necks of the crank mechanism.
What is another name for the crankshaft? Crankshaft is an abbreviated name. The full name of the part is crankshaft. It has a complex shape, the integral elements of which are the so-called knees. Another name is the knee.
What drives the crankshaft? The crankshaft is connected to the flywheel where the torque is transmitted. This part is designed to convert reciprocating movements into rotational ones. The crankshaft is driven by the alternate actuation of the pistons. The air / fuel mixture ignites in the cylinder and displaces the piston connected to the crankshaft crank. Due to the fact that the same processes occur in adjacent cylinders, the crankshaft begins to rotate.